The Ultimate Guide to SEO Indexing: Tips, Tricks, and Comprehensive Strategies | Linkboss
Pages not appearing on search engines can be incredibly frustrating for any website owner. However, there might be a reason for your invisibility to Google: SEO indexing problem.
Indexing in SEO refers to the process where search engines discover, analyze, and store web pages in their database if deemed worthy. It’s the first step in becoming visible on search engines. If a page isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in the search results.
To make sure your content gets the search engine’s attention, you have to follow certain steps. We can help. Today, we’ll discuss:
- What indexing is
- How indexing works
- Common indexing mistakes and their solutions
- Easy ways to accelerate indexing
Read on to learn how to make your site impossible to ignore—and discover how the right internal linking tool can accelerate your indexing.
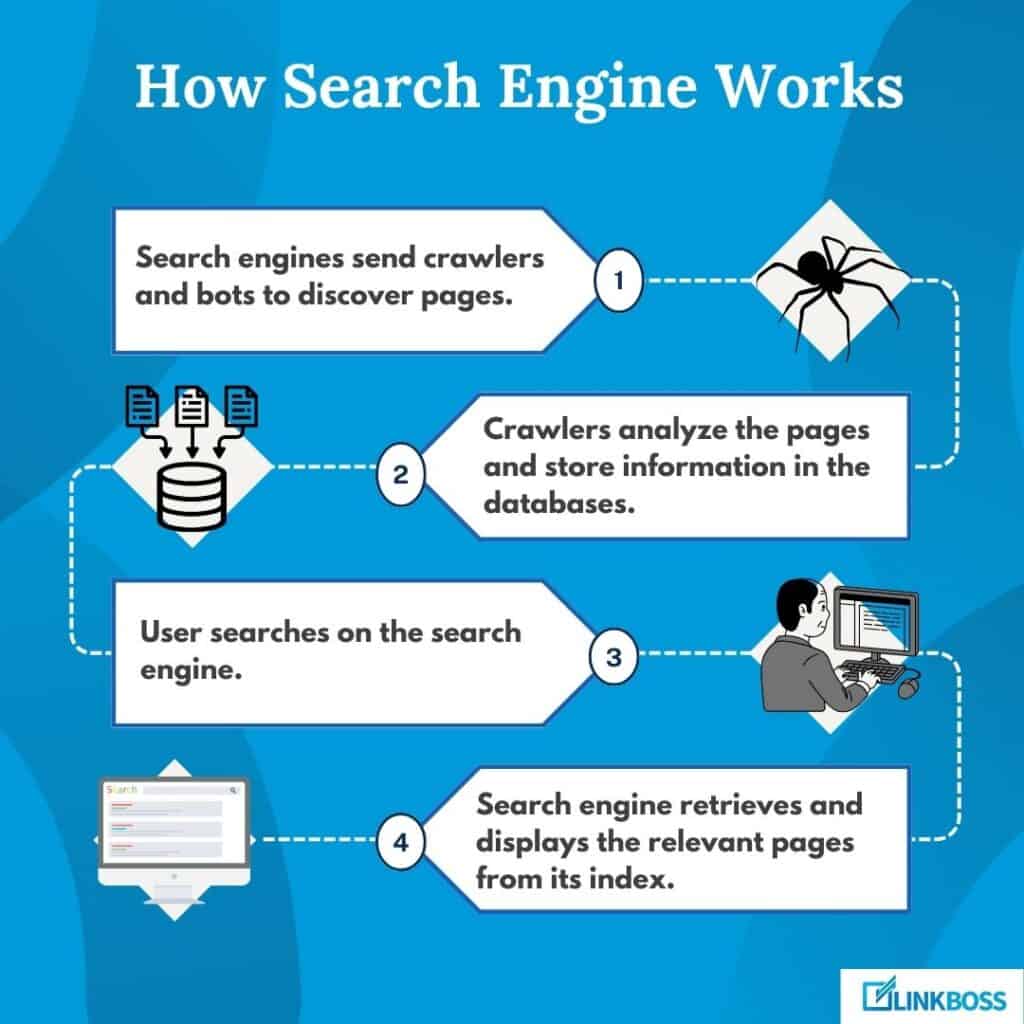
How Search Engine Works
Search engines use automated programs like crawlers and bots to discover pages. They analyze the pages and store information about them in their huge databases.
When a user searches in the search engine, it retrieves and displays the relevant pages from its index.
What Is Search Engine Index
A search engine index is a library of hundreds of billions of web pages. For example, Google’s index contains billions of web pages.
Google uses crawlers or bots to find web pages. When these crawlers find pages of websites, they make a copy of each page and admit it to Google’s index.
If the webpage isn’t in the index, Google won’t show it to users when they search on Google.
The Indexing Process of Google
Let’s break down the indexing process of Google:
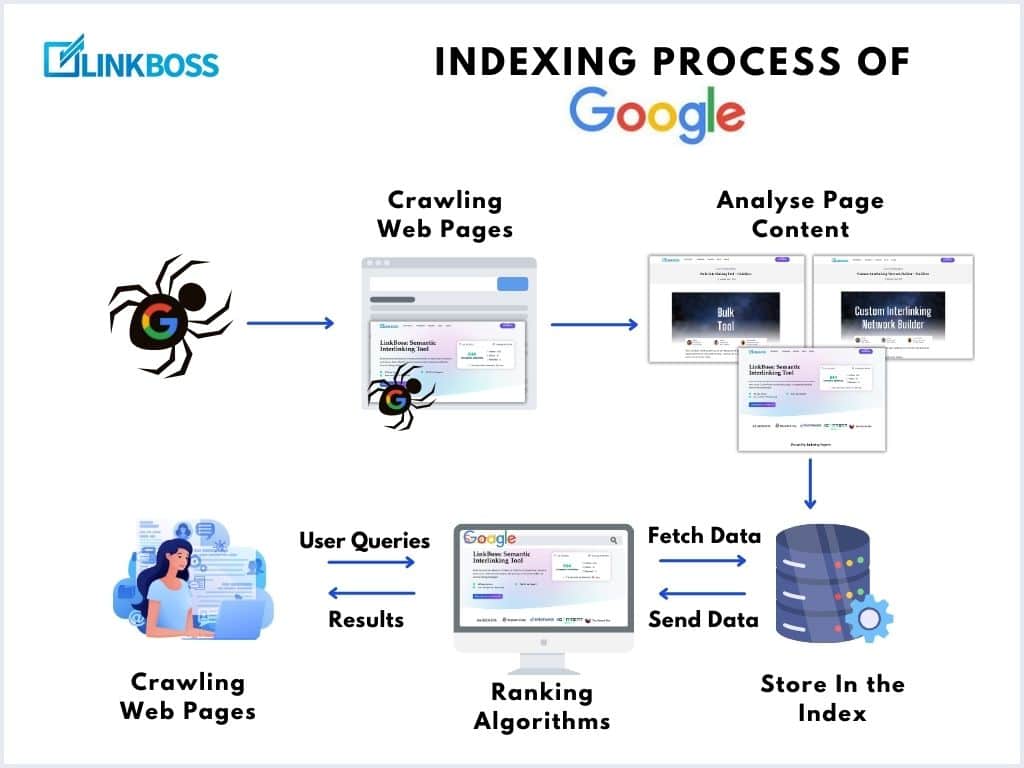
Crawling
Web crawling is the first step in how search engines like Google discover and understand web pages.
Google looks for web pages that exist online. There’s no complete list of all web pages, and millions of new pages are created every day, so Google has to search for them.
Google finds the web pages in 3 ways:
- Revisiting pages existing in its index
- Following links from known pages to new pages,
- Using a sitemap that website owners submit.
To find pages, it uses Googlebot. It visits your website and analyzes it without overloading it.
The Googlebot processes the page similarly to how your web browser does. It may run any JavaScript on the page to see the full content.
The Googlebot respects website rules and only visits pages the site owner has permitted. This crawling happens constantly to keep the Google index up-to-date.
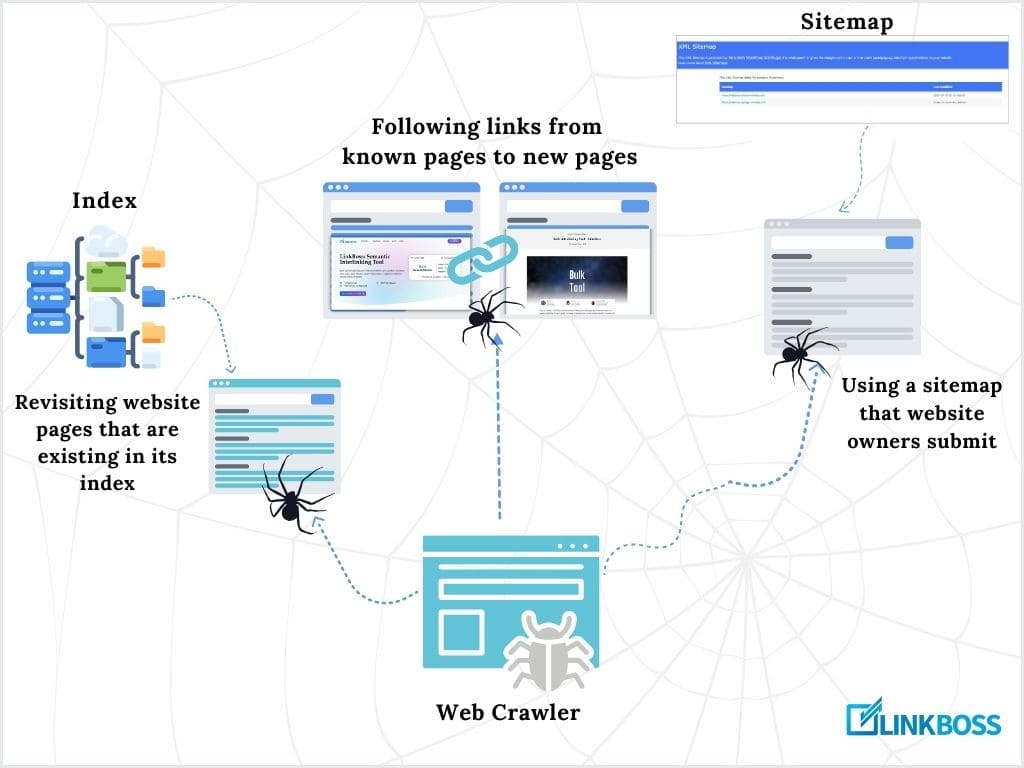
Indexing
The next step is indexing. It’s about storing and organizing information. Google will analyze the content and look at the page’s text, images, videos, and other elements.
It will go through the title, sub-heads, and alt text for images. Google also determines if the content is original or similar to other pages.
For groups of similar pages on a website, Google chooses one as the main or “canonical” page to show in search results.
All the info that Google gathers about the page is stored in its massive index. However, not every page it finds will be stored in the index.
Ranking
When you type a keyword into Google, it quickly looks through its index of web pages to find the most relevant pages.
Apart from the relevance and quality of the pages, the results can also be influenced by your location, language, and the device you’re using.
Different types of searches get different types of results. For example, a search for a local restaurant might show a map, while a search for a buying keyword like “best Samsung TV” might show text-based buying guides.
Difference between crawling and indexing
SEOs are often asked about the difference between crawling and indexing. And you’d be surprised how many get the answer wrong.
Go through the table so you’ll know what to say the that next time anyone asks you the question.
| Aspect | Crawling | Indexing |
| Main task | Discovers and collects information about web pages | Organize and store collected data for quick retrieval |
| Tool | Web crawler (Googlebot) | Large databases and server clusters |
| Process | Visits web pages, collects data, follows links, adds links to queue | Parses content for keywords and phrases, processes content for efficient storage, builds a database for the web, handles duplicate content |
| Frequency | Periodic frequency depends on site popularity | Ongoing process to keep the index up-to-date |
| Sequence | Crawling happens first | Indexing happens due to crawling |
How to Check If Your Website or Page is Indexed or Not
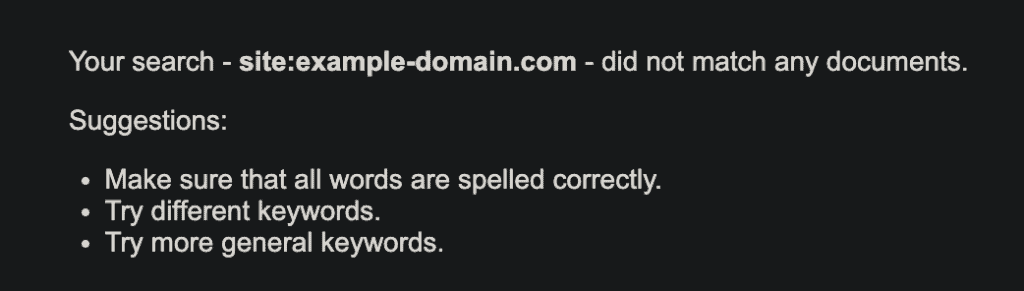
It’s quite easy to check if your website page is indexed. You can perform a site search. Go to Google and type “site:yourdomain.com” to see which pages are in Google’s index.
If your site’s not indexed, no results will show up.
If the site is indexed, Google will show them as search results:
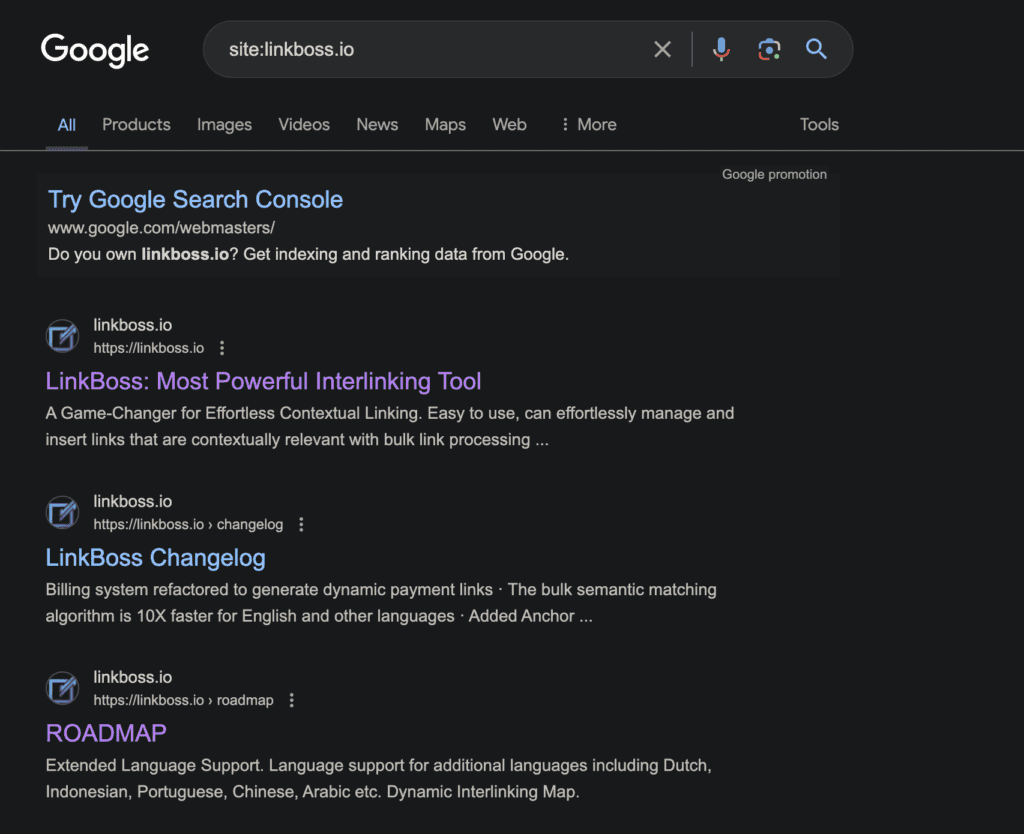
To find the indexing status of specific pages, you can use the same method, and just add the URL of the specific page to the search.
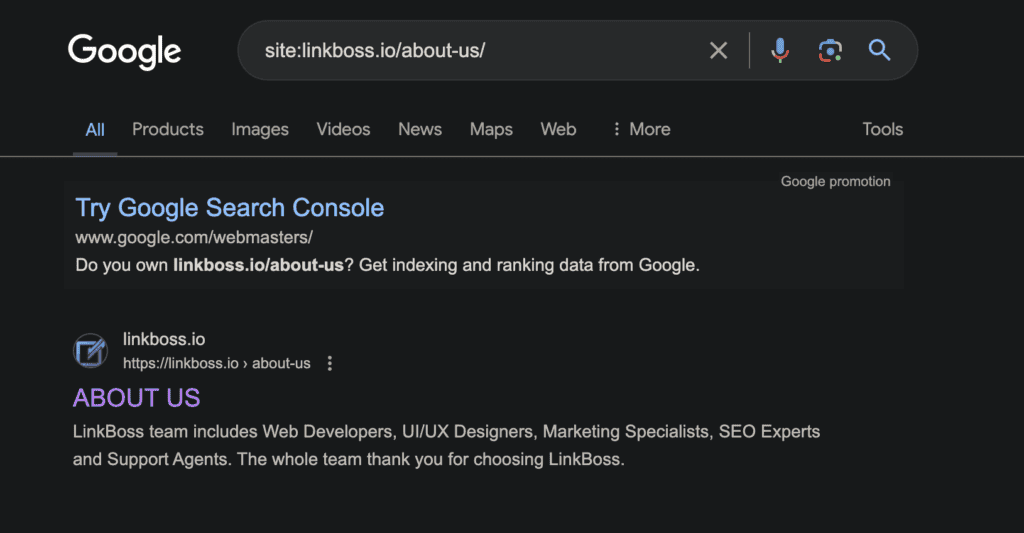
You can also use search console for that.
You’ll find a search bar to inspect URLs. Paste your link here.

If your page is indexed, it will show the URL is on Google.
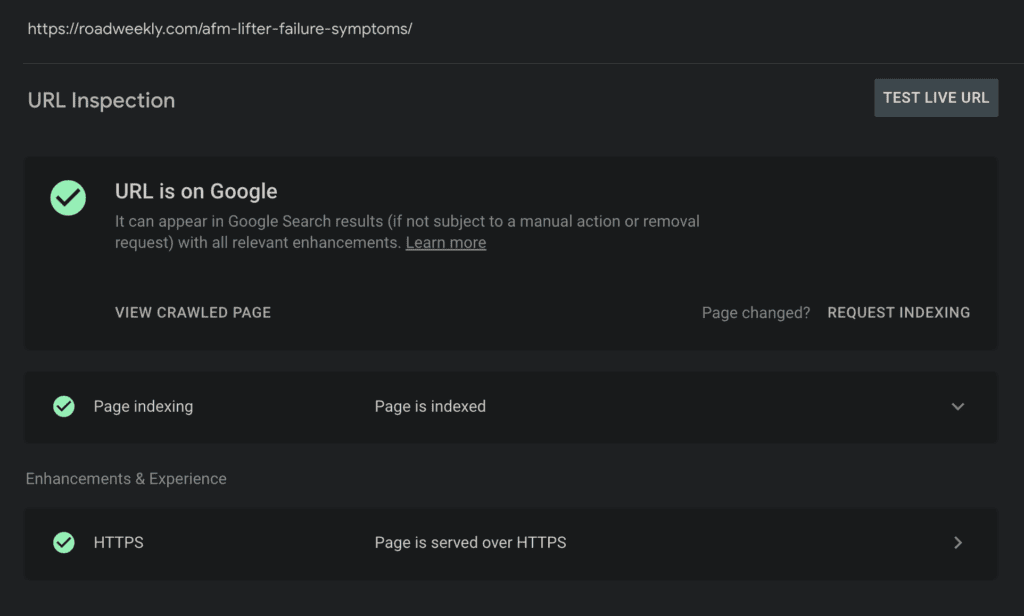
If the URL isn’t indexed yet, it will show that the URL is not on Google. For manual website indexing, you can then use the “Request Indexing” option.
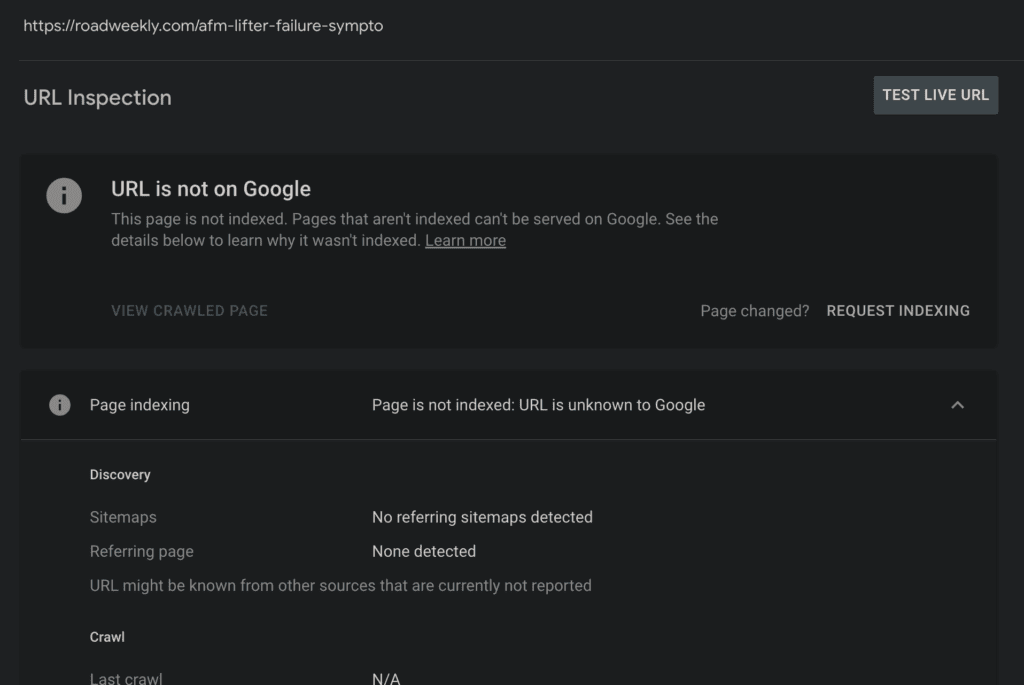
You might also see other errors in the GSC.
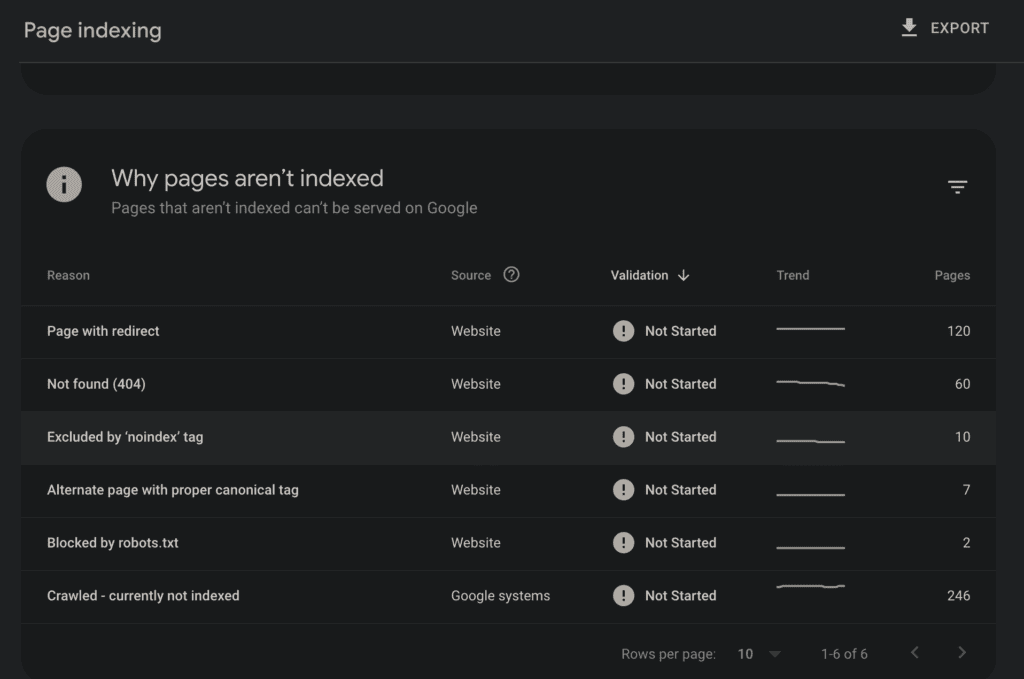
1. Crawled, currently not indexed.
That means Google has crawled the page but has decided not to index it.
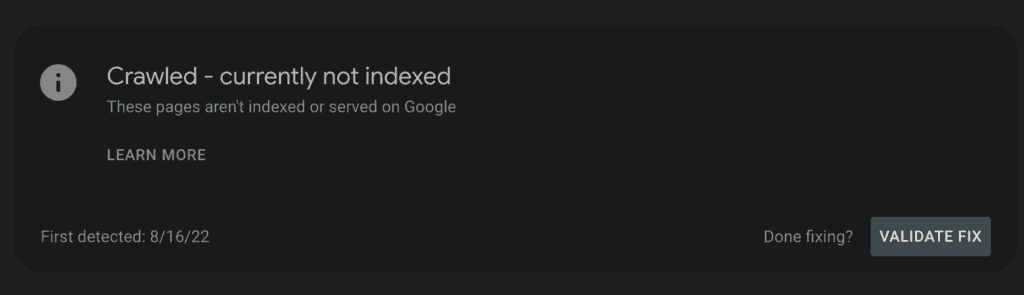
That happens when Google believes the page is not at the required standard for being indexed. But it’s a temporary status and might change in the future depending on the page’s quality and the site’s authority.
2. Not found (404)
A 404 error means the web page doesn’t exist on the server.
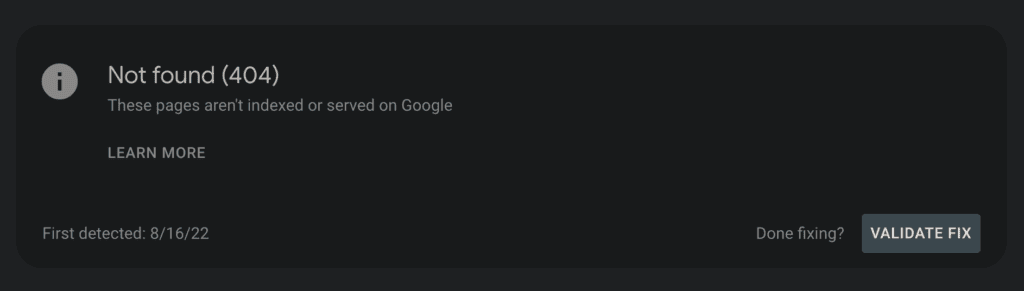
That can happen if the pages have been deleted or moved without a proper redirect. You should create a custom 404 page to guide users to return to the working sections of the website.
3. Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
That means the ‘no index’ tag has been used to tell the search engines not to include the pages in the search results.
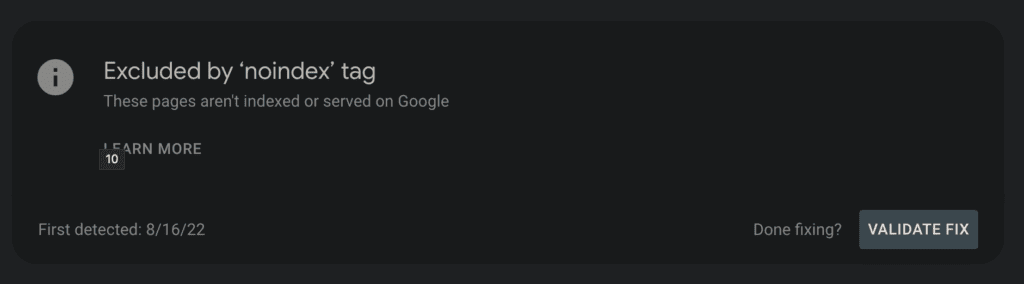
It’s used to hide private content from the search results.
4. Blocked by robots.txt
The robots.txt file is placed in the root directory to prevent web crawlers from visiting certain pages.
It’s important to use it carefully to not block important elements.
5. Page with redirect
Here, you’ll find the pages with redirects.
A redirect automatically sends visitors from one URL to another.
6. Alternate page with proper canonical tag
The canonical tag specifies the “canonical” or “preferred” version of a webpage when similar content exists on multiple URLs.
Why Isn’t Your Website Indexing?
There could be many reasons why your site is not indexing. Ask yourself the following questions to find your site’s issue.
Have you submitted your website’s sitemap to search engines like Google and Bing?
Submitting the sitemap should be one of the first things a site owner does. It helps Google find webpages easily and also makes the crawler spend more time on it, increasing the possibility of indexing pages.
So, if you haven’t submitted the sitemap yet, do so ASAP.
Are there any errors reported in Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools?
For errors, you can check the indexing report on GSC or Bing Webmaster Tools. If you find errors, try to fix them to help the pages index faster.
SCREENSHOOT
Is your website being blocked by the robots.txt file or meta tags?
Sometimes, webmasters accidentally block the crawlers from scanning the website with the robot.txt file.
Make sure your robot.txt file doesn’t have this:
The forward slash means it’s blocking all pages from being crawled.
The robot.txt file should look like this:
Are there any server issues affecting the accessibility of your website?
Server issues like slow loading, frequent and lengthy downtime, or errors can cause indexing issues.
You can use uptime monitoring tools and check error logs, and server response time to find if everything’s all right.
Is the content on your website unique, relevant, and free from plagiarism?
If the website’s content is plagiarised, too similar to other webpages, or simply of low quality, web crawlers may not index it. Tools like Copyscape and Grammarly can help check whether the pages are unique.
Are there any penalties or manual actions reported against your website by search engines?
Search engine penalties can cause problems with indexing. If a site receives a manual penalty, it will be harder to index new pages.
You can check for manual penalties in the Google Search Console (GSC). If there’s no manual penalty, it will show that no issues detected.
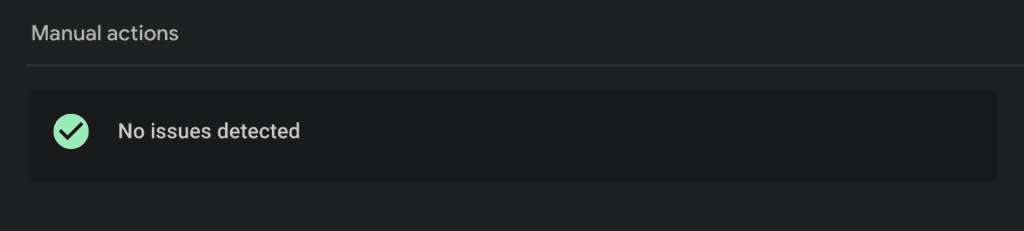
Also, if the website has been severely hit by an algorithmic update, it can also find it tough to index new pages. You can check GSC to see if there has been any drastic drop in traffic recently.
Is your website’s loading speed adequate?
Slow loading time can cause indexing issues. Google PageSpeed Insights can help you analyze page speed and identify issues to help you make the site faster.
Have you built any backlinks to your website to increase its visibility?
I’ve always found it difficult to grow new sites and faced indexing issues. However, one thing that always helped was high quality backlinks from authority sites.
A well-run campaign and some high-quality backlinks can make life a whole lot easier. Your contents start ranking faster, and all your pages start getting indexed in no time.
So, get some good quality backlinks and build site authority to resolve the indexing issue.
Is your website’s structure and navigation user-friendly and easily crawlable by search engines?
A well-structured website makes it easy for crawlers to navigate and find web pages. If the site structure isn’t navigation-friendly, crawlers will find it difficult to navigate, and the crawl budget will get wasted.
As a result, it can cause indexing issues. That’s why you should use a logical site hierarchy, XML sitemap, and relevant internal linking strategies to make indexing faster.
Are there any issues with your website’s mobile usability?
As Google uses mobile-first indexing, your site should be mobile-friendly to get indexed faster. Otherwise, they can also face indexing issues.
Google suggests using Google Lighthouse for testing mobile usability.
Search Engine Indexing Best Practices
What You Should Do for Google Search Engine Crawling
Here are some actionable tips for improving SEO indexing that you should implement in your site:
1. Submit an XML Sitemap to Google Search Console.
A good XML sitemap lists all the important pages of a website. Here’s how one looks like:
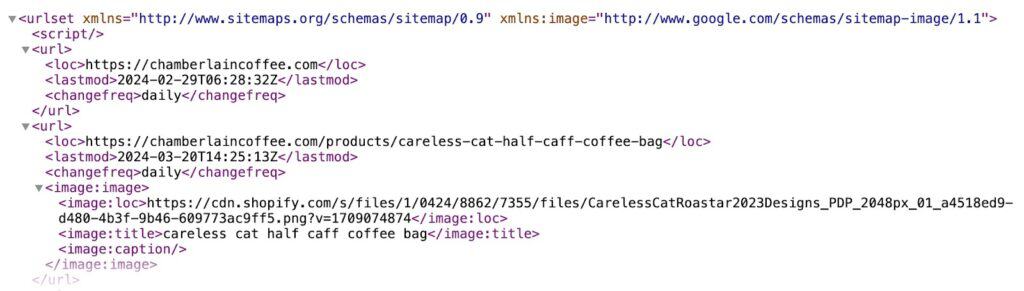
It makes sure search engine crawlers can easily find them and crawl them. As a result, the pages get indexed faster, and it also helps search engines understand the site better.
You can easily generate an XML sitemap through Yoast SEO and Rank Math plugins. Then, you can validate the sitemap.
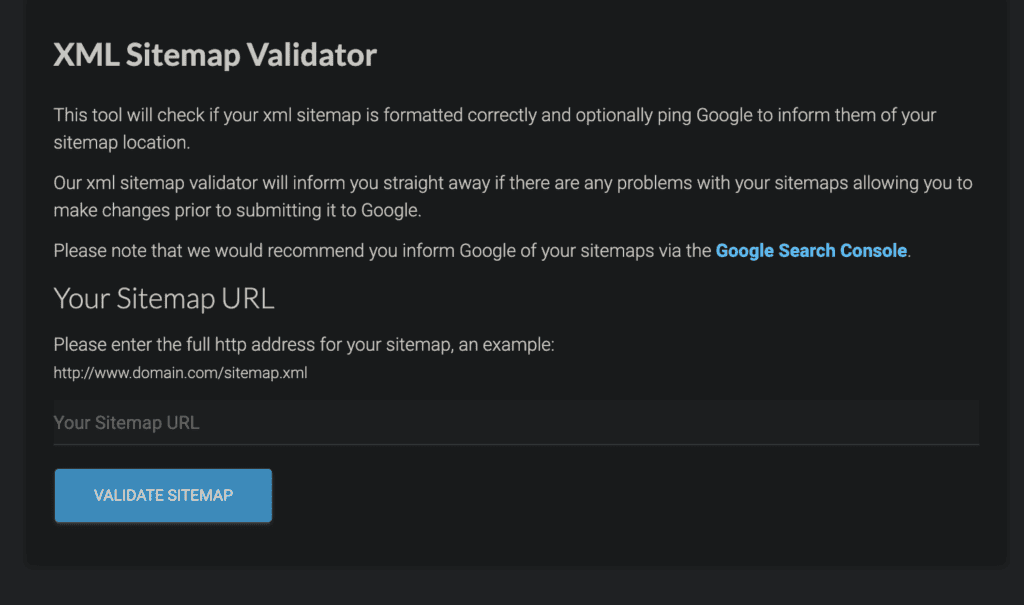
To submit the sitemap, you can paste the sitemap in ‘Sitemaps’ under ‘Indexing’ in the left sidebar.
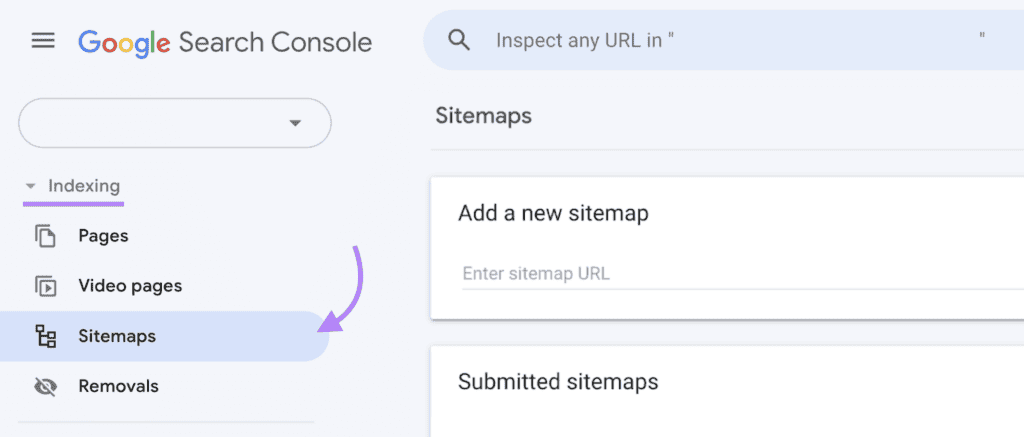
For larger sites, create multiple sitemaps. It’s better to keep a sitemap under 50,000 URLs and 50MB.
2. Optimize and properly configure your robots.txt file.
The robots.txt file determines which parts of the site crawlers can and can’t visit. Proper configuration is important for efficient indexing.
You can use Google’s robots.txt Tester in Search Console to check if it’s working properly.
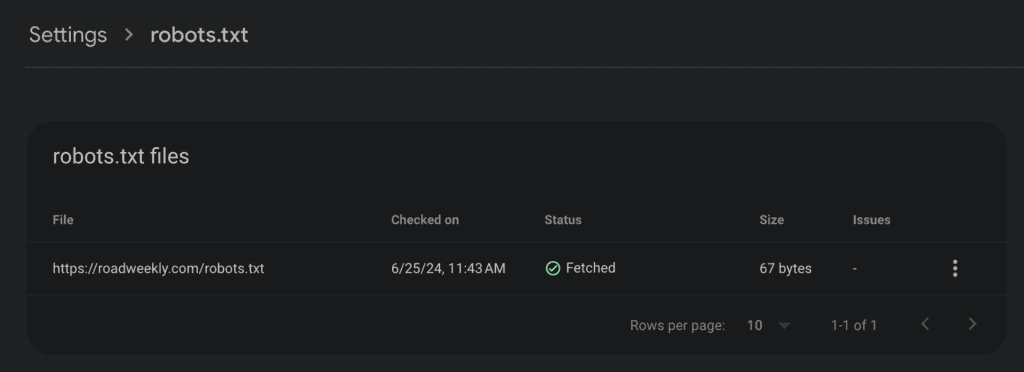
Don’t block important resources such as CSS, Javascript, and other essential elements. If you need to hide a page, it’s better to use the noindex tag rather than blocking it with robots.txt.
3. Ensure server uptime and reliability
If the server is down when the crawler visits the website, it can negatively impact indexing. That’s why ensuring high server uptime is important.
- Find a reliable hosting provider that can provide high uptime (99.99% or higher).
- Use plugins like Jetpack and Pingdom to monitor server uptime constantly.
- Make sure your hosting plan is big enough to handle spikes in traffic easily.
- Use backup servers or cloud solutions to maintain uptime if there’s an issue with the primary server.
- Regularly backup your site and create a disaster recovery plan if something goes wrong with the main server.
4. Implement a strong internal linking structure
Crawlers use internal links to follow and find new pages. Indexing issues can arise if the website has a poor internal linking structure.
Therefore, a strong internal linking structure should be created that helps users and crawlers navigate the site easily.
You can use breadcrumbs, contextual links, navigational links, sidebar links, and footer links to connect all the pages and offer Google a structured site to crawl.
Also, regularly review the old content and link to new pages. It will refresh the old pages and also help new pages index faster. Besides, periodically search for broken links and replace them with working ones.
5. Fix any crawl errors reported in Google Search Console
Check the GSC for any crawl errors. If there’s any issue with the pages, fix them and submit them again for evaluation.
6. Optimize site speed by compressing images and minimizing CSS/JavaScript.
Site speed can have a good impact on ranking and user experience. So, Google’s unlikely to favor sites that load slow.
Compressing images and minimizing CSS/JavaScript can help a lot. Here are some tips to implement:
- Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to compress images without losing quality significantly.
- Add lazy loading
- Use WebP format as it’s better for compression
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML by using tools like UglifyJS and CSSnano
- Implement browser caching for static resources to increase site speed
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to reduce the server response time
- Employ Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for faster mobile loading
7. Use a clean and simple URL structure.
A clean and simple URL structure helps search engines crawl and understand the content better. So, keep these things in mind:
- URLs should be short, descriptive and and clearly indicates the page content.
- Avoid using parameters when possible
- Avoid special characters
Example of bad URL: http://www.example.com/index.php?id=123&category=567
Example of Good URL: http://www.example.com/seo-tips-for-beginners
8. Ensure mobile-friendliness with responsive design.
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, it’s important to have a mobile-friendly site design.
Use responsive design and fluid grids and CSS Media Queries to ensure that content appears and works well on all devices.
9. Regularly update and publish new content
Refreshing old content and publishing new content makes crawlers visit your site more often. You can do the following to make crawlers love your site more:
- Make a content calendar to publish new content regularly.
- Update existing content to remove outdated information
- Add new sections to make the content better than the competitors.
10. Enable Gzip or Brotli compression
Enabling Gzip or Brotli compression for web resources can significantly reduce file sizes and improve load times. You can use either of them for your site.
Adjust your server settings by editing the appropriate files. For Apache, modify the .htaccess file, and for Nginx, update the nginx.conf file.
Focus on compressing files like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, XML, and JSON.
11. Create a custom 404 error page
A custom 404 page with easy navigation to the homepage or another relevant page can make the user experience better.
12. Analyze server logs to monitor crawler activity.
Server log analysis can tell you how search engine bots interact with your site. This will help you identify and resolve crawl issues.
I use two tools for that: Screaming Frog and Log File Analyzer.
- Analyze the frequency of crawls, crawl depth, and the most crawled pages
- Look for 4xx and 5xx status codes and redirects
- Check if all the pages in your sitemap are being crawled.
What You Should Do for Google Search Engine Indexing
These are some actionable steps you can take:
1. Create high-quality, unique content
You need to create high-quality, informative, and well-written content. Your content needs to answer questions, provide solutions, and offer a point of view that’s unique and valuable.
If your content does not meet these standards, you’ll have a tough time ranking. Here are some tips to make high-quality content:
- Address the pain points of the visitors
- Offer actionable solutions
- Showcase your expertise and offer real-life examples
- Update your content regularly to keep it relevant
2. Implement structured data (schema markup)
Structured data, also known as schema markup, provides information about a page and classifies its contents.
It makes it easier for search engines to understand the context of your content better, improving the chances of getting indexed.
There are many types of schema markup, including Article, Product, Event, Recipe, Review, and more. Choose the one that fits your content, as incorrect markup can harm your ranking.
3. Optimize title tags and meta descriptions
Optimizing title tags and meta descriptions can help rank your page higher in the search engine.
Use relevant keywords in them and keep the title tag under 60 characters to make sure they are shown fully in SERP.
4. Use canonical tags to address duplicate content.
Wrong canonical tags can prevent page indexing. If a canonical tag points to another URL, Google may not index the current page.
Check ‘pages’ in GSC to find the issue. You’ll find pages with “Alternate page with proper canonical tag” that have this issue.
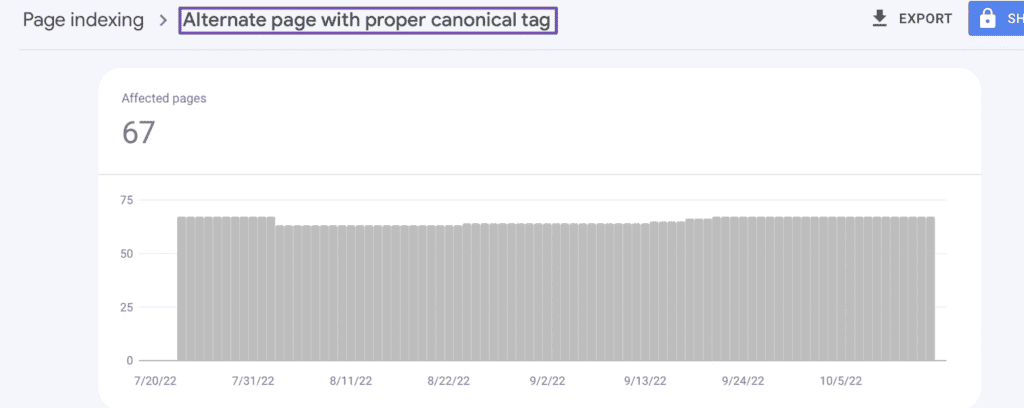
Fix the canonical tags to get them indexed.
5. Ensure clear and logical site architecture.
Clear and logical site architecture helps to make navigation and crawling easier. Here are some steps you can implement:
- Maintain hierarchy
- Clean URL structure,
- Use proper internal linking
- Employ breadcrumbs
- Submit sitemaps
These would help crawlers navigate the pages better and improve crawling efficiency.
6. Build high-quality backlinks
Backlink is the number one ranking factor, and that’s a fact. That’s why authority sites with powerful links can get their content indexed within minutes.
So, building high-quality backlinks can improve your site authority. That will lead to Google crawling your site more frequently and index pages sooner.
7. Promote content on social media
Google also uses social media to find new pages. By sharing your content on social media and getting clicks, Google can find and potentially index your pages.
8. Avoid thin content
Google likes pages that are to the point, but thin pages that offer no value will often remain unindexed. So, make sure the pages aren’t thin and have enough valuable content.
Monitor indexing status in Google Search Console
Google’s search engine offers great insights for free, and you should make use of it.
Regularly check the indexing status of your pages using Google Search Console (GSC). Use the Index Coverage report to monitor the indexing status of your pages. If any issue comes up, you can take prompt action to prevent any negative SEO impact.
Check for and resolve manual actions
You can check for manual penalties in GSC.
If you’ve been handed out a manual penalty by google, resolve it as soon as possible and submit a reconsideration request.
Ensure HTTPS is enabled
HTTPS encrypts data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website. It protects sensitive information like payment details and login credentials. Implementing HTTPS is important for both SEO and gaining visitor trust.
Common SEO Indexing Issues You Can Face
There are some common SEO indexing issues you need to know about. But no worries, they have easy fixes too.
Duplicate content
Duplicate content can significantly harm your site’s potential. However, it’s easy to find duplicate contents.
In Google Search Console’s Index Coverage report, you can identify duplicate content problems on your site.
- “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” means you haven’t specified a preferred version for duplicate URLs.
- “Duplicate: Google chose a different canonical than the user” indicates that Google decided to ignore your canonical tag and chose their preferred version.
- “Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical” means Google decided to ignore the canonicals you submitted through your XML sitemap.
Here, are some other ways you can detect duplicate content:
- Use Screaming Frog to find duplicating titles and meta descriptions
- Use plagiarism checkers for quick checks on suspected pages
- Check for product descriptions that are the same across multiple pages
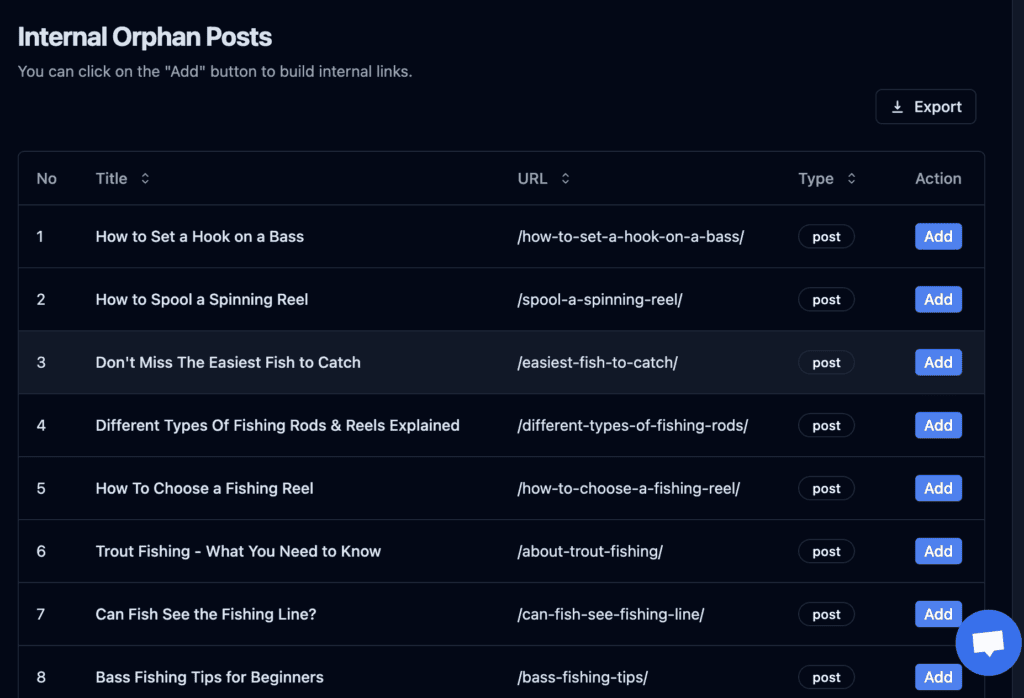
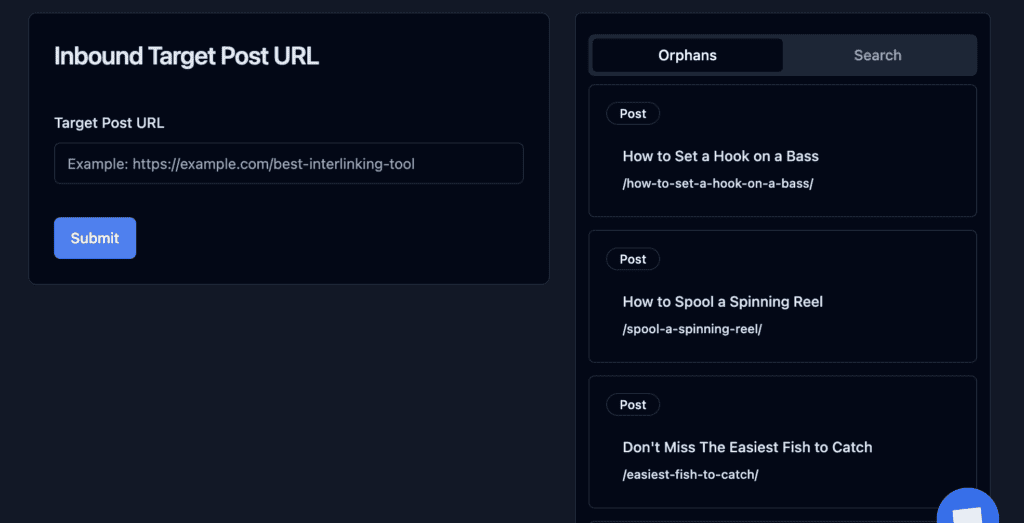
Orphan pages
Orphan pages aren’t good for SEO and can cause indexing problems. As no pages link to them, it can be hard for crawlers to find them. And if crawlers can’t find them, they can’t index them.
Linkboss shows all the orphan posts on their report section. You can also create interlinks right from the dashboard for the orphan pages.
Blocked resources
Sometimes webmasters use noindex tag and robots.txt file to block important pages by mistake.
To detect blocked resources:
- Check your robots.txt file for disallow directives
- Use a crawler like Screaming Frog to scan your site for noindex tags
After that remove disallow directives in your robots.txt file if necessary, and remove noindex tags from important pages.
Google’s indexing bugs
Google’s indexing bugs are temporary technical issues that can cause a large drop in indexed pages. You might see a sudden drop in the number of indexed pages or pages disappearing from Google.
In this case, you can do nothing except wait for Google to fix the issue. Keep an eye on Google’s official channels for announcements and updates.
Thin content
Thin content can cause indexing issues as it usually doesn’t have unique content and doesn’t meet Google’s minimum requirement. You can identify thin content through these signs:
- Pages with very little text (Under 300 words)
- High bounce rates in analytics
- Low time-on-page metrics
You can fix the problem by adding relevant information to the page or merging several similar thin pages into one.
How You Can Accelerating Google indexing
Accelerating Google indexing is possible. GSC and Google News can help you with that. Find out how:
In-depth guide on using Google Search Console for indexing
Here’s how you can use the inspection tool:
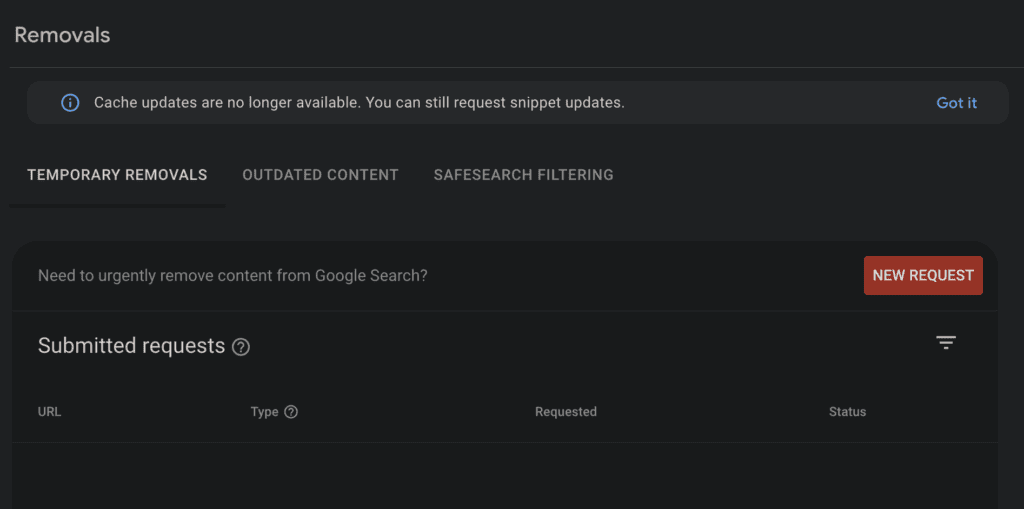
- URL Inspection Tool: It allows you to check the indexing status of individual URLs on your site. The inspection tool also helps to submit pages manually for indexing.
- Coverage Report: The Coverage report informs you about the indexing issues across your site.
- Sitemaps: You can use the “Sitemaps” options to submit a sitemap and help Google crawl your pages..
- Remove URLs: If there are similar pages, you can remove them from the site through the “Remove URL” option.
Google News for Faster Indexing (if applicable)
Google News is a powerful platform that can help improve your site’s indexing speed. You can apply for Google News for your site.
And if approved, it will help your pages get indexed really fast. You can submit your sitemap to Google News. This is separate from your regular sitemap.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using LinkBoss.io for Better Indexing
There are many ways that Linkboss can help you in better indexing.
Finding orphan pages
Orphan pages can really hurt a site’s SEO and may often go unindexed, wasting all the efforts that went into making the content.
You can go to report, find all the orphan links on your site, and build interlinks for them.
Creating internal links
Creating relevant and natural interlinks takes time. But, no more! Linkboss has made creating interlinks a breeze.
With the inbound link tool, you can create interlinks for any posts within seconds.
Bulk Internal linking
Building interlinks for large sites with thousands of pages takes hundreds of hours. But Linkboss has brought that down to mere minutes, as you can create interlinks in bulk with a few clicks.

Building Silo
Creating a silo is one of the most effective interlinking strategies and helps with indexing a lot. The Linkboss silo tool helps you connect relevant articles and build powerful silos within a couple of minutes.
Content, backlinks, and SEO are important for a site’s success. But if it has indexing issues, nothing else will matter. So, follow the given tips to ensure indexing and make your content visible to search engines.
Internal linking is key to indexing as it plays a vital role in enabling crawlers to find your content.
LinkBoss has made the process extremely easy as it allows you to find orphan pages, create relevant interlinks quickly, and manage internal links at scale. Also, it has a free trial period, and you have nothing to lose.
So, try LinkBoss today! See your pages getting indexed faster than ever!