Internal Linking for E-commerce: How to Boost E-Commerce SEO
When most people think about E-commerce SEO, they focus on keywords, backlinks, or content. And yeah, those things matter. A lot.
But here’s what gets overlooked: internal linking.
In fact, for large e-commerce sites, internal linking can make or break your organic visibility. Google doesn’t magically know which of your 50,000 product pages is important.
It relies on your internal link structure to figure that out.
And it’s not just for Google. A smart interlinking strategy also improves user experience. It makes it easier for shoppers to discover related products, find categories, and move through your funnel.
If your e-commerce site isn’t set up with the right internal linking strategy, you’re leaving rankings (and revenue) on the table.
Why Internal Linking Matters For E-Commerce SEO?
In my opinion, internal linking is step #1 for scaling an e-commerce site’s SEO.
So, what’s the reason? Without the right internal links, products and categories remain hidden. Google and customers will never find them.
Here’s why it’s such a big deal for online stores:
First, internal links help Google discover all of your pages.
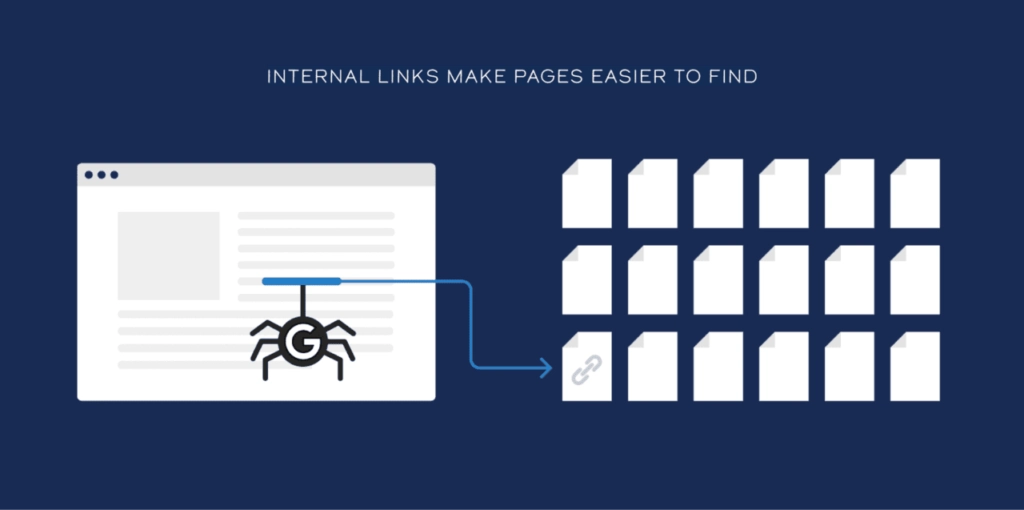
Without them, you’ll often end up with orphaned products pages with no links pointing to them. And if Google can’t find a page… it won’t get indexed.
That’s lost traffic right there.
Second, internal links distribute authority across your site.
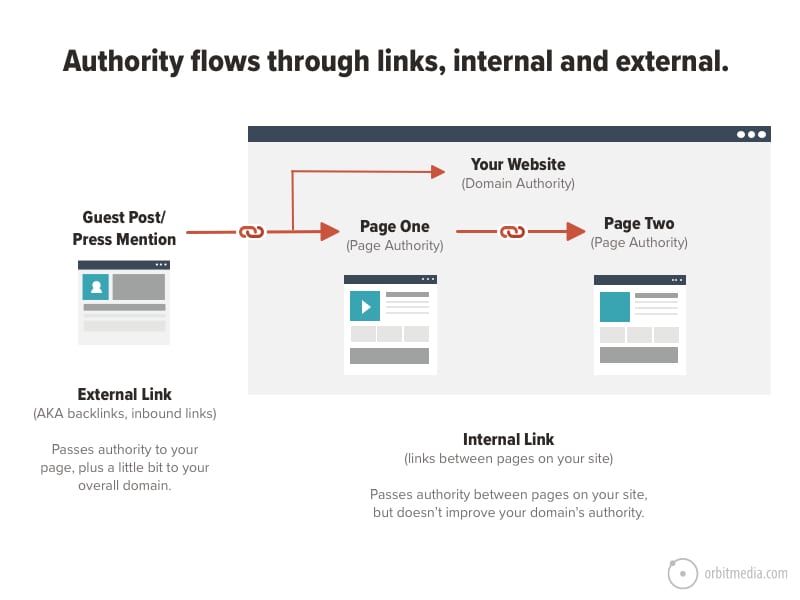
Your homepage is usually the strongest page on your site. By linking from it and from your categories you push SEO value down into your product pages. That’s how you get them ranking for high-intent keywords.”
Third, it’s not just about Google. Internal linking also improves user experience.
Think about it: a shopper lands on a product… and sees links to related categories, bundles, or complementary products. That keeps them browsing, lowers bounce rates, and increases sales.”
“And here’s the big one: internal links directly impact revenue.
They don’t just help rankings, and they guide customers to buy.
Cross-sells, upsells, and related products all rely on smart linking. Done right, this can make the difference between a casual visit and a big order.

Fundamental Internal Linking Tactics for E-commerce SEO
If you’re new to e-commerce SEO, internal linking might sound technical.
However, it’s actually one of the simplest ways to boost rankings and sales. In this section, we’ll cover two core tactics every beginner should know:
Linking Strategies for Category Pages
Let’s start with parent-to-child category linking. Think of your categories as a family tree:
The parent is a broad category, like ‘Shoes’.
The children are subcategories, like ‘Running Shoes’, ‘Formal Shoes’, or ‘Sandals’.
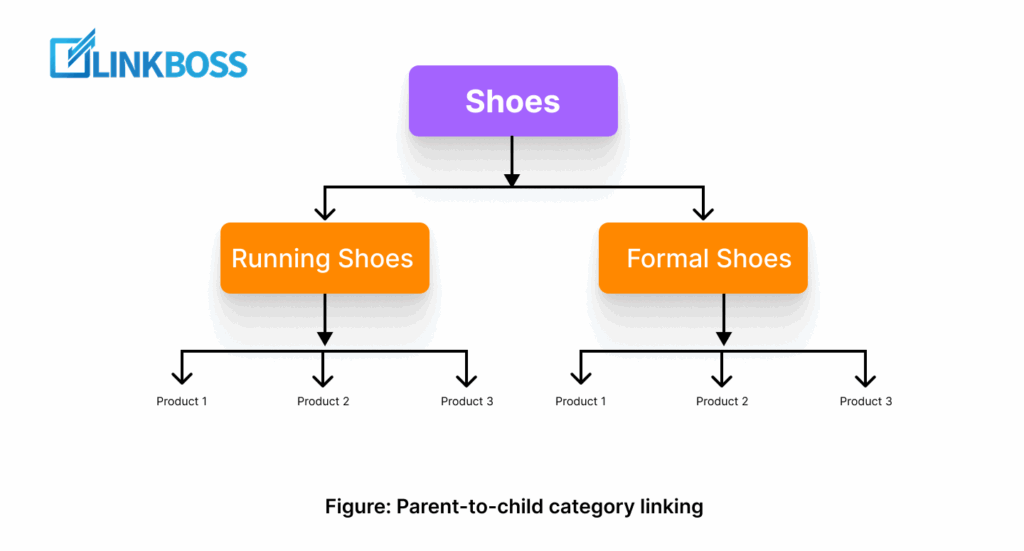
By linking from the parent page to each child category, and then from those child categories down to the products, you’re creating a clear path for both shoppers and search engines.
Next is cross-linking between related categories.
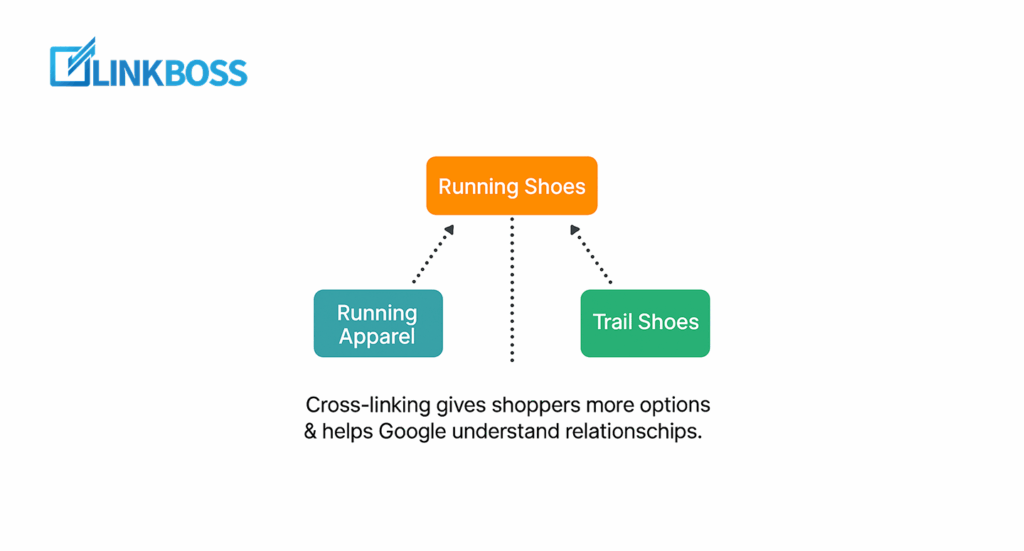
Imagine a customer is browsing the ‘Running Shoes’ category. That page can also link to related categories like ‘Running Apparel’ or ‘Trail Shoes’.
This not only gives shoppers more options but also helps Google understand the connections between your product ranges.
Advanced Internal Linking Strategies for E-commerce SEO
You’ve learned the fundamentals of internal linking. Now, it’s time to level up with advanced strategies that can take your e-commerce SEO to the next stage. Here, we will cover:
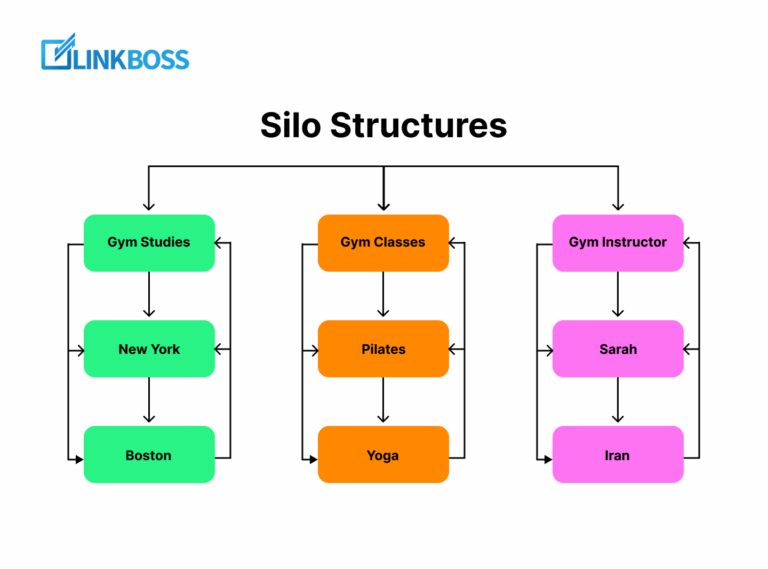
SEO Silo Structures for Online Stores
A silo is simply a hierarchical structure that connects your categories, subcategories, and products in a logical way.
Think of it like this:At the top, you have your parent category, let’s say ‘Shoes’.
Under that, you have subcategories like ‘Running Shoes’ or ‘Formal Shoes’.
And beneath those, you have the individual products.
This flow would be like this-
Parent → Subcategory → Product
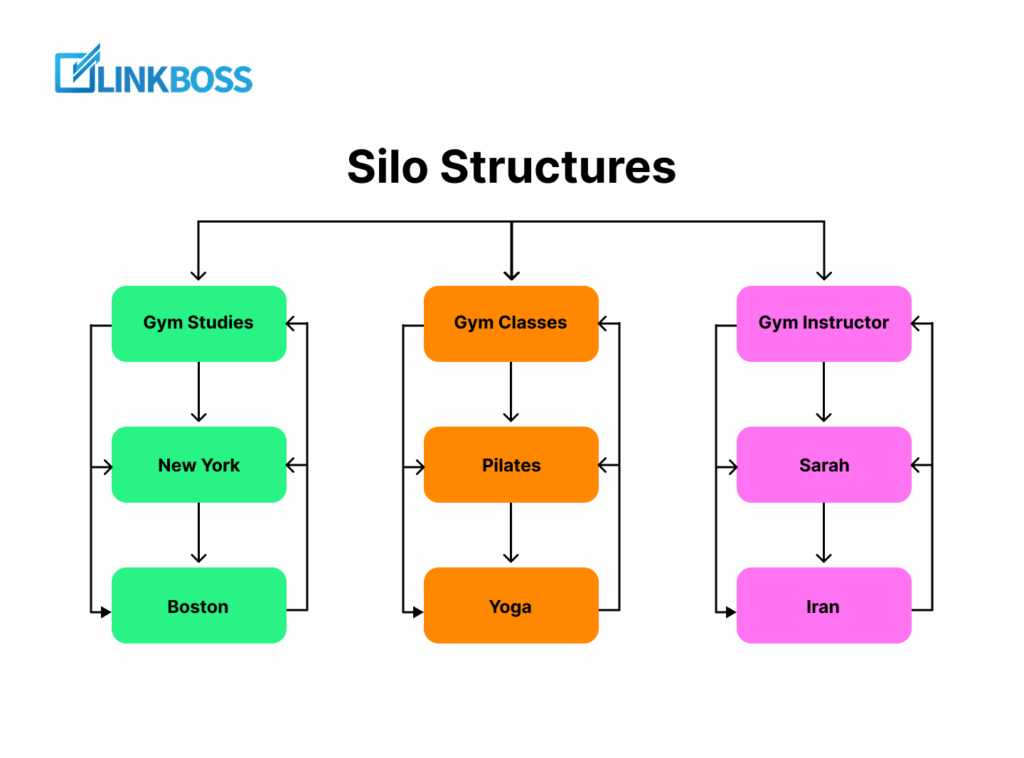
makes your site easy to navigate, for both Google and your customers.
Optimizing Anchor Text for Internal Links
Now, we’re diving into one of the most overlooked, but super important parts of internal linking: anchor text optimization.
In anchor text optimization, the starting point is using exact match and partial match anchors for internal links.
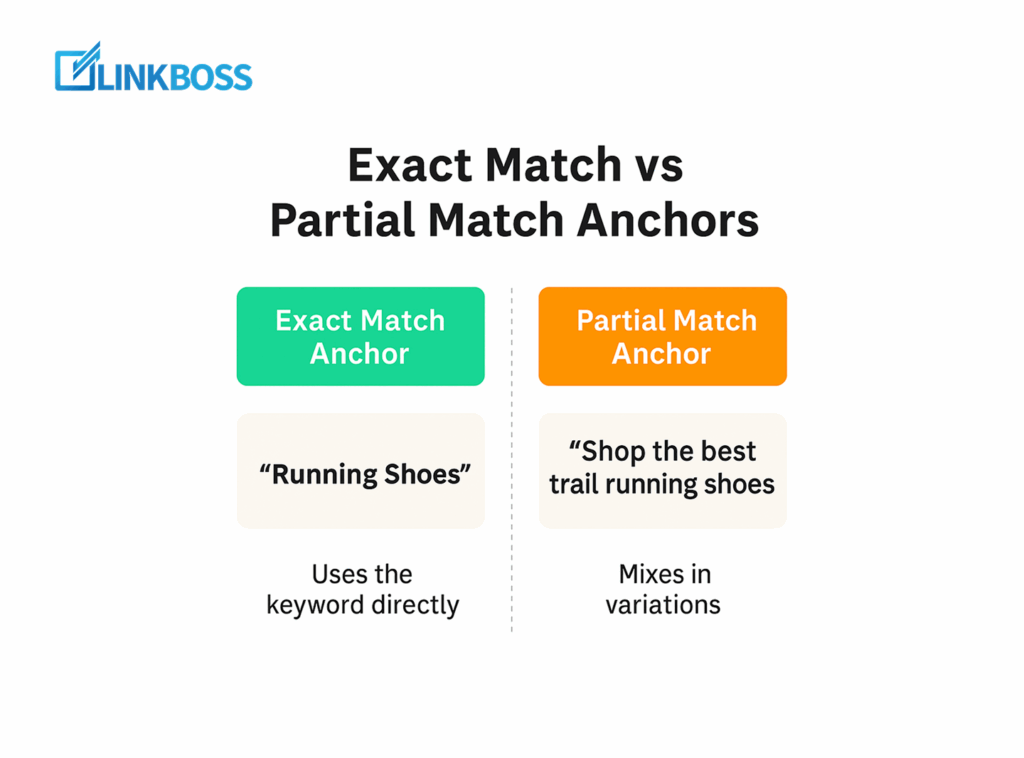
An exact match anchor uses the keyword directly. Example: linking to your category page with the text ‘Running Shoes’.
A partial match anchor mixes in variations. Example: ‘Shop the best trail running shoes’.
Both are useful, in which an exact match sends a strong SEO signal, while a partial match keeps your linking natural signal.
Now here’s a warning: don’t overdo it.
If every link to your category page says ‘Running Shoes’, Google might see that as spammy or manipulative.
So, what should you do? Mix it up with natural variations like ‘lightweight running gear’, ‘trail shoes collection’, or even a simple ‘shop now’ where it makes sense.
Best Practices about Anchor Optimization in E-Commerce SEO
- For category pages: Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchors, but vary them slightly.
- For product pages: Keep it specific. Instead of generic ‘click here’, use anchors like ‘Pro Runner 3000 Treadmill’.
Content-to-Product Linking Strategy
Blog content often attracts backlinks and traffic that product pages never get.
By adding smart internal links from your blogs to your products, you can pass that authority straight to the pages that drive revenue.
So how do you link effectively?
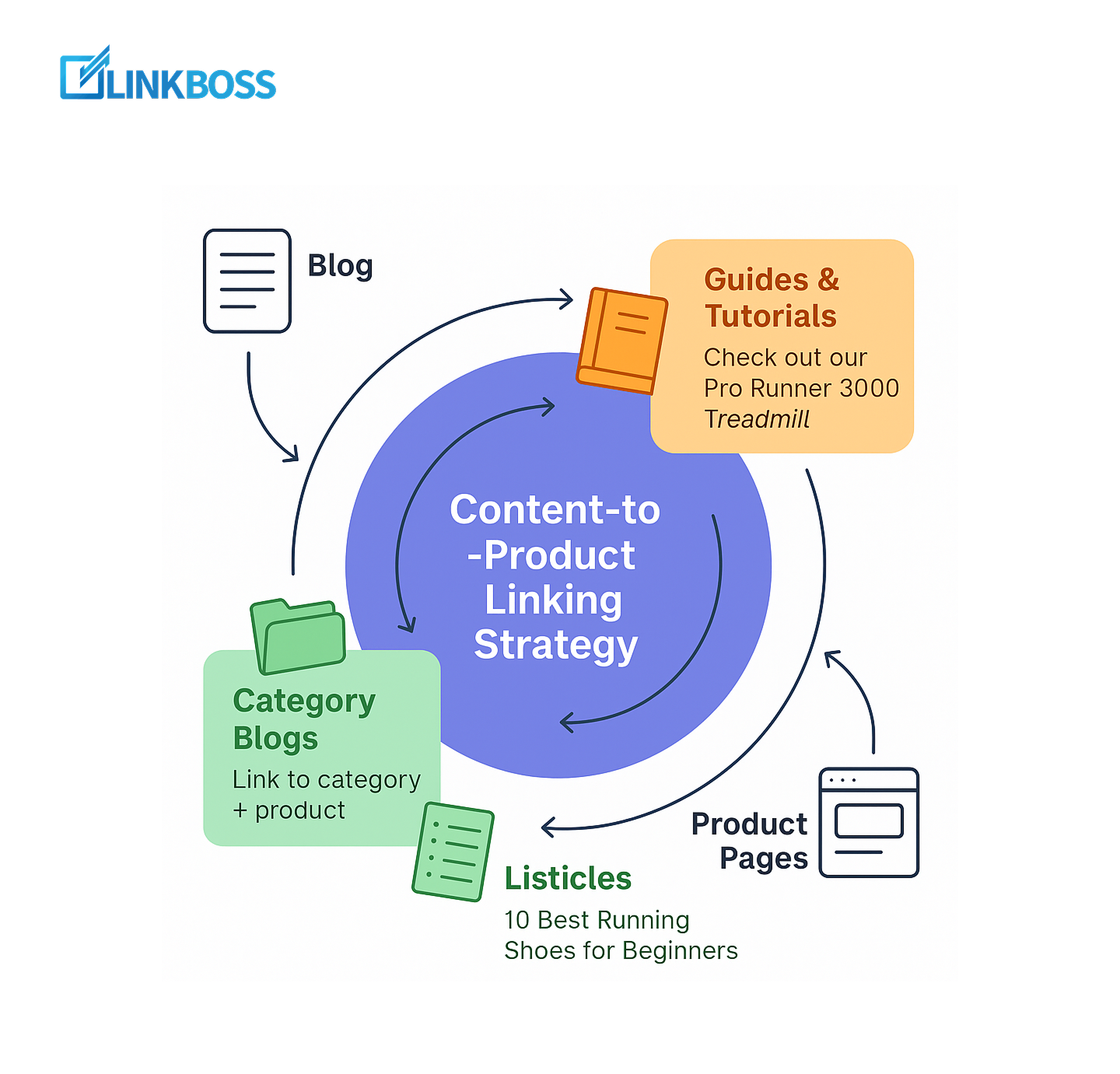
- In guides and tutorials, naturally mention your products. For example: ‘Looking for the best gear? Check out our Pro Runner 3000 Treadmill.’
- In listicles, like ‘10 Best Running Shoes for Beginners’, link each mention directly to the product page.
- In category-focused blogs, link back to the related category page as well as individual products.

Deep Linking Strategy for Large E-Commerce Sites
If you run an e-commerce site with thousands of products, this strategy can dramatically improve crawlability and rankings.
Deep linking means connecting directly to pages buried deep in your site structure, and not just your homepage or top categories.
For example, instead of only linking to ‘Shoes’ → ‘Running Shoes’, you also link directly to a specific product like ‘Pro Runner 3000 Trail Shoe’.
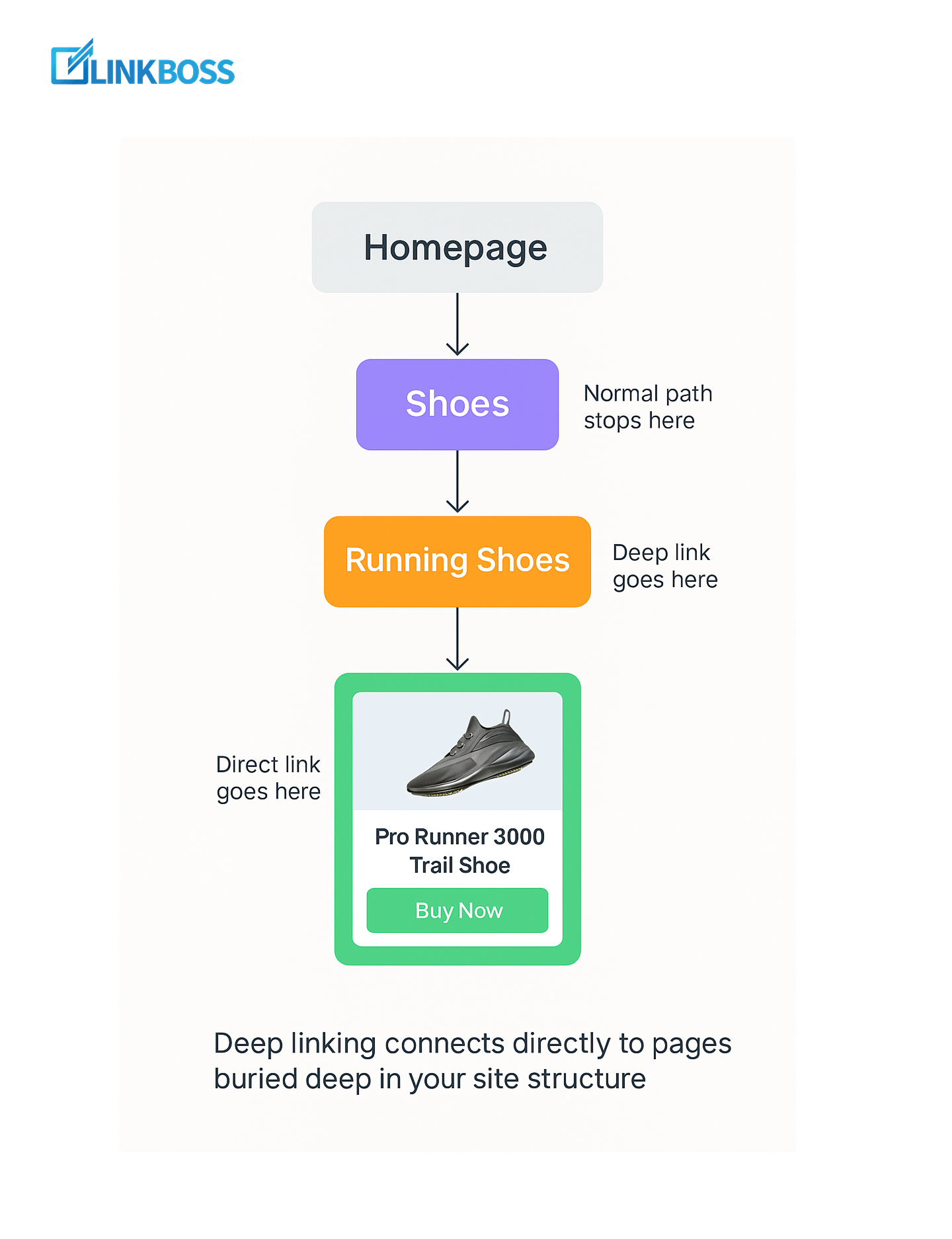
This makes sure that important products and subcategories don’t get lost several clicks away from the homepage. Here’s the problem with large stores: search engines can miss or take forever to crawl deep pages.
Deep linking solves this by:
- Making products easier for Google to find.
- Ensuring link equity flows beyond just top-level categories.
- Reducing the risk of orphaned pages that never get indexed.
Automating Internal Linking with Tools
When you’re managing hundreds or thousands of products, manual linking just isn’t scalable. That’s where automation comes in.
This is quite impossible and not worth investing time in manually creating internal links. What if your website contains a massive amount of links, like 10K pages? What could you do in that case? In 2025, manually creating internal links is not a viable solution.
You can do it strategically, with intelligent internal linking with an AI-powered tool like LinkBoss.
LinkBoss provides you with the opportunity to integrate with various tools in multiple ways. You can link like 200 pages within a second.
The most interesting aspect is that you can interlink based on silo structures and visualize all orphan pages instantly.
In 2025, it’s time to take full advantage of the AI-powered tool.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
We’ve almost talked about strategies that make internal linking powerful. However, just as important is knowing the mistakes that can hinder your e-commerce SEO.
Let’s examine the most common ones and learn how to avoid them.
Orphaned Product Pages
One of the biggest mistakes is leaving orphaned product pages, as well as pages with no internal links pointing to them.
These pages are practically invisible to Google. And if Google can’t find them, they won’t rank.
Always ensure that every product is connected to at least one category and, ideally, a related product or blog post.
Excessive Footer Links
Another issue is excessive footer links. Many stores attempt to cram every category and product into the footer, believing it will improve SEO.
But in reality, it creates clutter, dilutes link equity, and often confuses both Google and your customers.
Suggestion: Keep your footer clean and focused, featuring only the most essential links.
Random Internal Links Without Hierarchy
A third mistake is adding random internal links without a clear structure.
For example, linking from a product page to an unrelated category just to ‘add a link.’ This doesn’t help SEO, and it disrupts the user journey.
Internal links should always reflect a logical hierarchy. They should guide shoppers naturally through your store.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What strategies scale internal linking across thousands of SKUs?
For extensive catalogs, the best approach is to combine automation with a structured approach. Use tools like LinkBoss or Screaming Frog to auto-suggest links at scale, but design clear silos.
Is linking seasonal products risky for evergreen SEO pages?
It can be if you overdo it. Evergreen category pages should always maintain stable, keyword-focused links. Seasonal links can be added for promotions, but they should be rotated out once the campaigns end.
Which anchor text variations prevent over-optimization signals?
Avoid repeating the same keyword every time. Instead, use a mix: exact-match anchors for clarity, partial matches for variety, and natural CTAs like “shop now” or “explore collection.”
What KPIs matter most when auditing large-scale internal links?
Key metrics include crawl depth, percentage of orphan pages, distribution of links to money pages, and user engagement. These show both SEO strength and real UX value.
Should faceted navigation links be crawled or blocked?
Most faceted filters generate duplicate or thin pages. Therefore, they should be blocked using robots.txt or the noindex tag.
Final Word
Internal linking isn’t just about sprinkling a few links here and there.
It’s about building a structure that helps both users and search engines. If Google can’t easily find, crawl, and understand the relationships between your product and category pages, you’re leaving rankings on the table.
Instead, you want a flat, organized structure.
One where your most important categories get consistent internal links. And one where link equity naturally flows to the products that matter most for your business.
At the end of the day, internal linking is one of the most underrated levers in e-commerce SEO. It’s technical, it’s strategic, and if you do it right.