Internal Links vs External Links: Which One is More Important?
Internal vs external links: which should take priority in your SEO strategy? While external links, especially backlinks, often take center stage in SEO discussions, internal linking shouldn’t be overlooked.
Both internal and external links pack a punch for your site’s authority and visibility. But here’s the thing…
To nail your linking strategy, you’ve to understand the difference between internal and external links and how to use them properly.
You can’t just focus on one and ignore the other. Optimizing both internal and external linking strategies is the key to unlocking your site’s full potential.
This guide will go over their differences, their impact on SEO, and the best practices for both. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for creating a balanced linking strategy to dominate your niche.
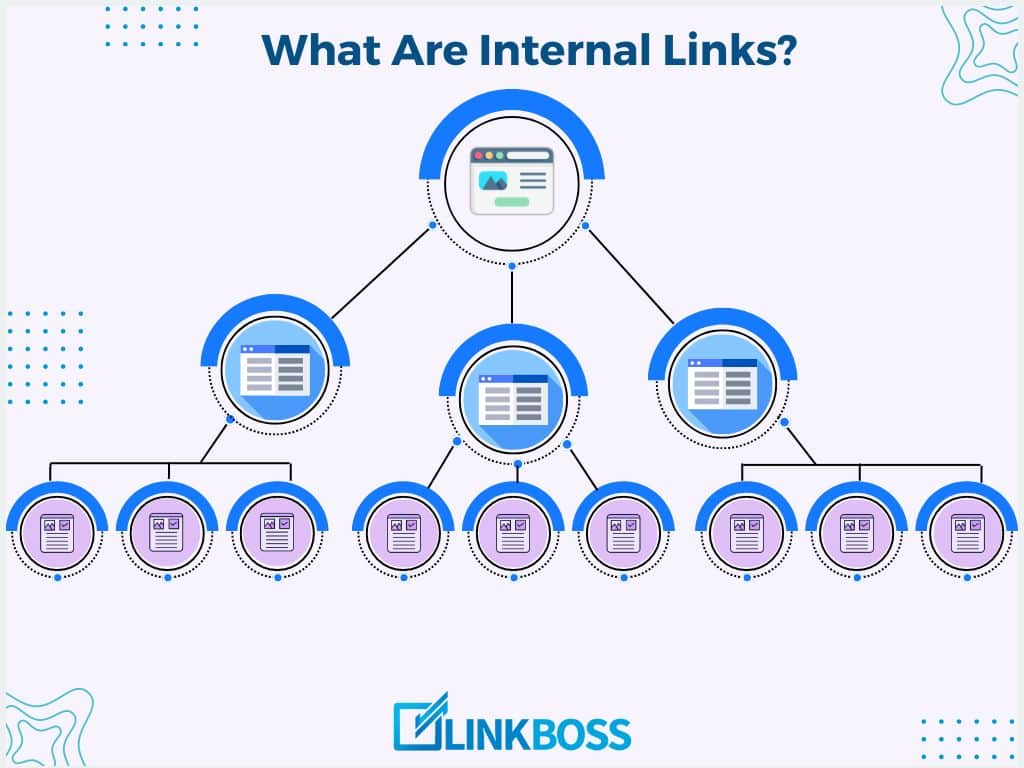
What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks within a website that lead users from one page to another on the same domain. These links help users navigate websites and discover related content. This keeps them engaged and exploring your site for longer.
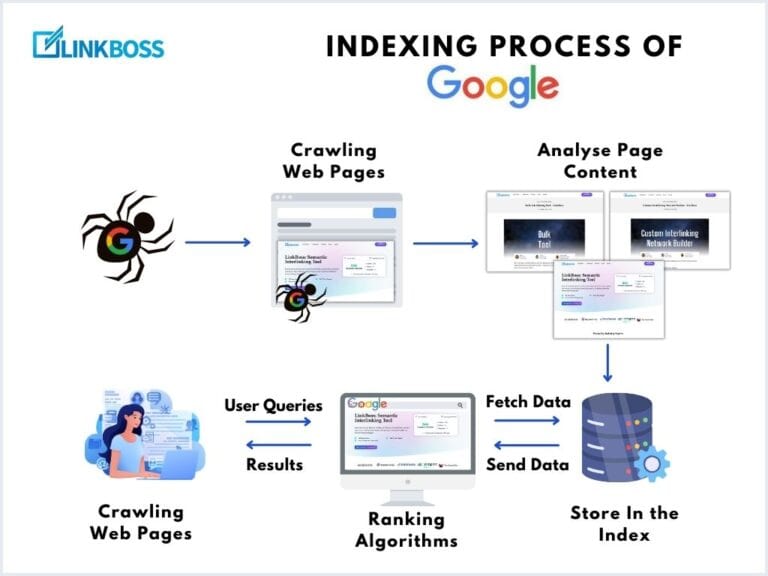
Search engines like Google use internal links to understand your website’s structure and hierarchy. Strong internal linking helps them discover all your website’s pages and grasp the relationships between them.
Want to see your current structure? An interactive site visualizer can map your entire internal link network—making it easy to spot gaps and opportunities.
Examples Of Internal Links
Internal links are everywhere. Ever clicked a link on a website and stayed on the same site? Those are internal links.
For instance, on an e-commerce site, you might find a link from a product page to a related category page or from a blog post about summer fashion trends to a collection of summer dresses. Let’s take a look at some examples.
1. Navigation Menu Links
Take a look at the top navigation menu on our homepage. Those links all point to different pages within our website. These are also internal links.
Links Within Blog Posts To Related Articles
Another common internal linking example would be the links within blog posts to related articles.
“Read More” Links At The End Of Blog Excerpts
These links take the user to the full version of that blog post.
Sidebar Links To Popular Posts
Links in your sidebar that point to popular content on the same website are also internal links.
Footer Links To Important Pages Within the Website
Footer links to important pages take users from one page on a website to another page on the same website. These links provide easy access to key sections like “About Us,” “Contact,” or “FAQs.”
What Are External Links?
External links, also called outbound links, are links that take you to a page on a different domain from your website. The term “external link” actually has another definition.
When another website links to a page on your website, that is also called an external link. We commonly refer to those links as backlinks or inbound links. Search Engine Land published an article on outbound link back in August 2023.
Even though the headline can be a bit misleading, check out the last part. Also, if you have noticed, I made the words “Search Engine Land” clickable so you can check out the article immediately. This is called external linking.
When done right, outbound links can be a powerful tool. Search engines also use these links to understand your website and how it connects to other information online. External links can be categorized into two main types:
1. External Incoming Links (Backlinks/Inbound Links)
These are links from other websites that point to your site. They’re crucial for SEO because they’re like trust signals from other sites. Think of them as citations from respected sources in your field.
The more high-quality backlinks you have, the greater the authority and credibility your website gains in the eyes of search engines like Google. Take a look at the backlink profile of LinkBoos.io:
You can’t directly control backlinks. Other websites decide to link to you based on the value and relevance of your content.
However, there are strategies to encourage backlinks, like creating high-quality content and guest blogging on relevant websites. I will discuss this further later on.
You can easily see the number of backlinks and which sites are linking to your website with Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
You can also find backlinks using tools like Ahrefs and Semrush. These tools can help you understand your backlink profile and identify areas for improvement.
2. External Outgoing Links (Outbound Links)
External outgoing links are the opposite of backlinks. These are links from your website to other websites. They provide additional value to your readers and help establish your site’s relevance and authority. Take a look at this example:
These links can lead users to additional resources that answer their questions in more detail. This is especially helpful if your content doesn’t have space to cover every aspect of a topic.
Examples Of External Links
Have you ever clicked a link that took you to a completely different site? Those are external links.
For example, a blog post about SEO might link to Google’s official guidelines or a reputable industry study to support its claims. Some common examples of external links include:
Citations Of Sources In Blog Posts
Links To Partner Websites
Social Media Profile Links
References To Industry Reports Or Studies
These are all external links because they lead you to a different website. Now that you know what outbound links are and why you use them, it is time to look at some other types of external links.
NoFollow and DoFollow Links
Let’s explain NoFollow and DoFollow Links. They’re not as complex as they sound, but they matter.
NoFollow
NoFollow links are like giving a lukewarm recommendation. You’re saying, “Check this out, but don’t put too much stock in it.” You can usually tell if a link is NoFollow by inspecting the link.
Right click on the link in the browser and select “inspect”. If you see rel=”nofollow” then the link is a NoFollow link. Search engines see these links but don’t give them much weight.
High-traffic sites often use NoFollow to manage their link juice. It’s a way to avoid potential penalties for excessive linking.
DoFollow
DoFollow links are the standard. If you do not see rel=”nofollow” then it is a dofollow link. They’re like giving a full endorsement. These links pass authority from your site to the linked page. In SEO terms, we call this “link juice” passing.
Note: Don’t use NoFollow for internal links on your own site. That’s like telling search engines to ignore your own content.
Which One To Use?
Choosing between NoFollow and DoFollow is a big part of any SEO strategy. It’s all about balancing authority distribution and user experience.
Both types can be valuable to your readers. The key is using them strategically. Think about your goals for each link you add.
Is it purely for user benefit?
- Consider NoFollow.
Want to boost another site’s authority?
- Go with DoFollow.
Remember, it’s not just about SEO. Links should always add value for your readers. Use these attributes to shape how search engines see your site’s connections. But never at the expense of user experience.
Internal vs External Links: Core Differences
Here are the key differences between internal and external links:
| Topic | Internal Link | External Link |
| Definition | Links to pages within the same website | Links to pages on other websites |
| URL structure | Relative URLs (e.g., /about.html) or absolute URLs within the same domain | Full URLs including domain (e.g., https://example.com/page) |
| Control | Full control over linked content | Limited or no control over linked content |
| SEO impact | Improves internal site structure and SEO | Can provide SEO benefits through backlinks |
| User experience | Keeps users on your site | May direct users away from your site |
| Loading speed | Generally faster | May be slower, depends on external site |
| Reliability | More reliable, less prone to broken links | Can become broken if external site changes |
| Security | More secure | Potential security risks if linking to untrusted sites |
| Tracking | Easier to track user behavior | May require additional tools to track off-site clicks |
| Credibility | Builds internal authority | Can enhance credibility by linking to reputable sources |
The Impact Of External And Internal Links On SEO
Ever wonder why some sites crush it in search rankings while others flop? Links play a huge role here. Both types of links contribute to SEO in different ways. Links are like the currency of the web.
External links build your authority, while internal links strengthen your site from within. Nail both, and you’ll see your rankings climb. Let’s break it down.
How External Links Boost Your SEO
Getting external links is like getting a vote of confidence from another website. The more high-quality sites link to you, the more Google and other search engines trust you.
However, quality matters more than quantity. A few links from respected, relevant sites can do more for your SEO than hundreds of low-quality ones.
Remember, links from sites in your niche or related industries carry more weight. They tell search engines that you’re a trusted source in your field.
Why Internal Links Matter for SEO
Internal links are often overlooked, but they’re seriously powerful. They help search engines understand your site structure, spread link juice across your pages, and keep visitors on your site longer. If I had to narrow down three key benefits, those would be:
- Internal links help search engines find and rank your content more effectively, so you get more visitors.
- Linking relevant content together keeps users engaged, resulting in more page views and clicks.
- Well-linked websites help users take the actions you want them to, so your conversions go up.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
Internal linking is a crucial part of any solid SEO strategy. It’s not just about throwing in random links – there’s an art to it. It’s not rocket science, but it does require some thought.
By strategically connecting your content, you’re not just helping visitors navigate your site—you’re also giving search engines valuable clues about its structure and the importance of various pages.
Internal Linking For Better SEO
Google uses these links to understand your site’s structure and content relationships. It’s like a roadmap for search engines, helping them crawl and index your site more effectively. Here’s how to make the most of internal linking.
1. Create A Solid Site Structure
Think of your site as a pyramid. Your homepage is at the top, with category pages below and individual posts at the bottom. This hierarchical structure makes it easy for both users and search engines to navigate your site.
It also helps establish the relative importance of different pages. Those higher up in the structure are typically seen as more important.
2. Use Your Cornerstone Content
Got some killer pieces? Make sure they’re well-linked throughout your site. Cornerstone content represents your best, most important content on a specific topic.
By linking to these pages often, you’re signaling to search engines that these are highly valuable pages. This can help boost their visibility in search results.
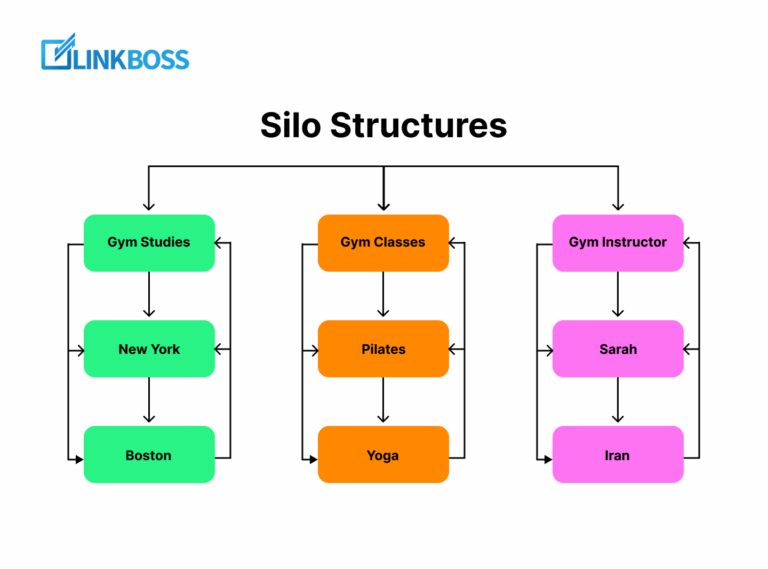
Matt Diggity did an interview with Kyle Roof a year ago where Kyle showed a simple yet effective silo technique. Check out this video:
We also have a detailed guide describing what are interlinking silos if you are interested.
Say you have a target page and want that to rank higher on the SERPs.
You need to write 5 or more supporting articles. After that, you’ll have to internally link all the supporting articles together and then link to the target page from each.
They’re all linking to the target page, and they’re also linking to each other. Kyle does it sequentially. For example,
- Post A links to Post B
- Post B links to Post A and Post C
- Post C links to Post B and Post D
- And so on…
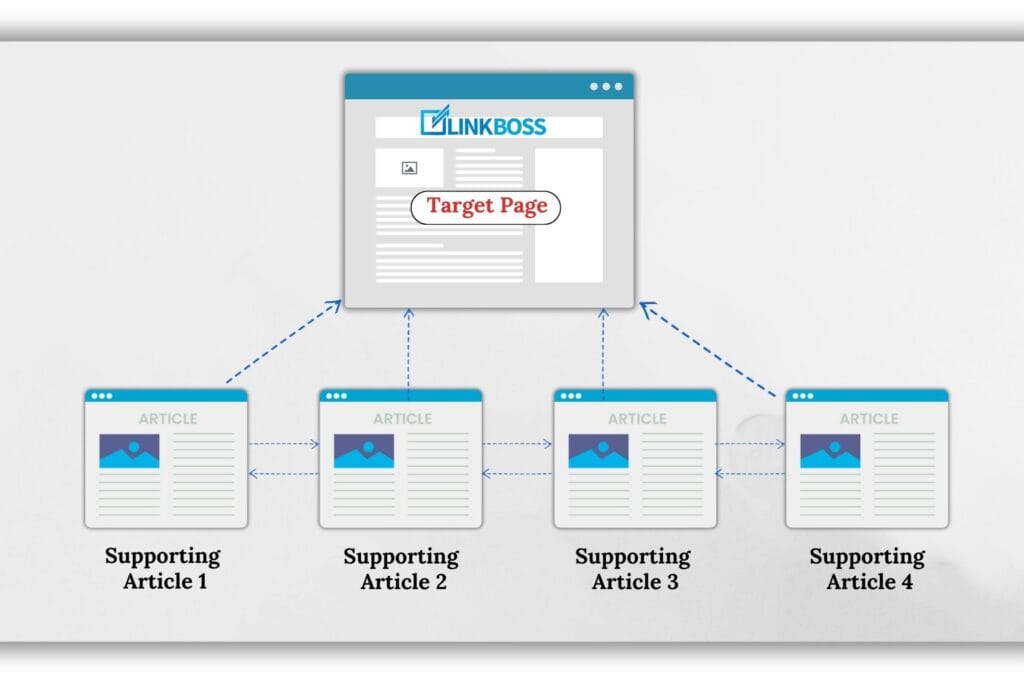
To complete the internal linking circle, Kyle also tries to get a link from the target page to one of the silo pages. This helps pass link juice better.
Note: I know it is hard to do it manually, but LinkBoss makes it much easier to implement silos like these.
3. Keep It Relevant
Don’t just link for the sake of it. Make sure the connections make sense. When you link to related content, you’re providing value to your readers and helping search engines understand the relationships between your pages. This relevance is key – irrelevant links can confuse both users and search engines.
4. Optimize Anchor Text
Use keywords in your anchor text but keep it natural. Your anchor text should give users and search engines a clear idea of what the linked page is about.
Using relevant keywords here can boost SEO but overdoing it can look spammy. Aim for a mix of exact-match keywords, related terms, and natural phrases.
5. Balance Your Link Distribution
While it’s natural to have more links pointing to your homepage and main category pages, don’t forget about your deeper content. Linking to these pages can help search engines discover and index them.
While manually balancing your link distribution can be time-consuming, LinkBoss makes it a breeze. Our AI-powered tool doesn’t just focus on your homepage and main categories – it intelligently distributes links to your deeper content too.
This helps search engines discover and index all your valuable pages, not just the top-level ones. Give LinkBoss a try. With our smart linking algorithm, you can build a balanced internal link structure that boosts your entire site’s SEO.
Tools And Plugins To Automate Internal Linking
Internal linking is crucial for SEO, but manually adding links can be a pain. Thankfully, there are tools and plugins that can automate this process. Some popular internal linking plugins are:
- LinkBoss
- All In One SEO (see LinkBoss vs AIOSEO comparison)
- Internal Link Juicer
- Yoast SEO (see our LinkBoss vs Yoast comparison)
- Rank Math (see our LinkBoss vs Rank Math comparison)
These tools scan your content and suggest relevant internal links. But you still have to add them manually, except for LinkBoss. Our internal link building tool takes the guesswork out of link building and makes the whole process smoother.
Automatic Internal Linking In WordPress
LinkBoss uses AI to analyze your content and find the best linking opportunities. It doesn’t just suggest links – it adds them automatically. This means you can build a solid internal linking structure in a few clicks.
The beauty of LinkBoss is its simplicity. It’s like having an SEO expert working 24/7 on your site. See why LinkBoss is better:
LinkBoss.io doesn’t just add random links. It’s smart about it. It considers factors like relevance, anchor text, and link placement.
This ensures your internal links actually boost your SEO, not just clutter your content. And unlike some other tools, LinkBoss.io gives you full control.
You can review and edit its suggestions before they go live. This balance of automation and control is what sets it apart.
What Makes LinkBoss.io Stand Out?
- Uses AI to build semantic interlinks at scale.
- SILO with topic clusters.
- Smart contextual linking.
- Bulk interlinking.
- Fresh content generation.
If you’re tired of manually adding internal links, give LinkBoss.io a shot. It will show you how easy it is to use in the next section.
How To Use LinkBoss to Build Internal Links in WordPress?
Automatic internal linking in WordPress is no longer just a luxury; it’s a necessity if you want to stay ahead in the SEO game.
Let me demonstrate how easy it is to automate internal linking with LinkBoss. You can either watch this video.
Best Practices for External Linking
Let’s switch our focus to external links—both outbound and inbound. They’re a crucial part of any solid SEO strategy and getting them right can make a big difference to your site’s performance.
When we talk about external links, we’re looking at two main types:
- Outbound links
- Inbound links, aka backlinks
Both types play a role in how search engines view your site and can impact your rankings. But how do you make the most of them? Let’s break it down.
External Links For SEO Ranking
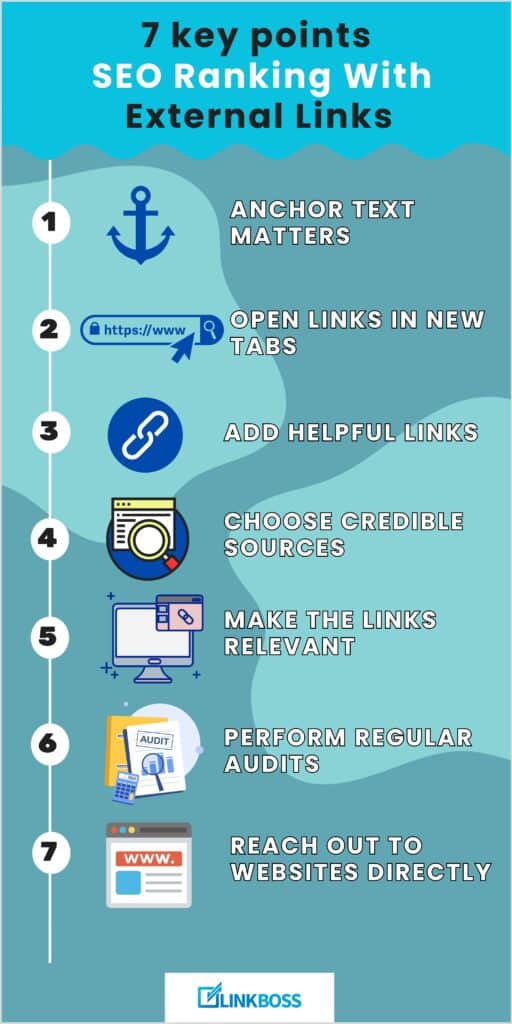
Here are seven key points to remember when using external links for SEO ranking.
1. Anchor Text Matters
When you’re choosing anchor text, think about relevance first. If you’re linking to a page about dog grooming, don’t use “click here” as your anchor text. Instead, try something like “expert dog grooming tips.”
Also, don’t go overboard with the exact match keywords. Mix it up. Use variations, long-tail phrases, and even branded terms. This looks more natural and helps you avoid any potential penalties for over-optimization.
2. Open Links in New Tabs
This is a simple trick, but it can really boost your engagement rates. By using the ‘target=”_blank”‘ attribute, you can give readers new information without them leaving your site.
Users spend more time on your site, bounce rates decrease, and overall user experience improves. It’s a win-win situation.
3. Add Helpful Links
When you add links, always ask yourself, “Does this add value for my reader?” If the answer is yes, go for it. If it’s a no, maybe reconsider.
Remember, it’s not about how many links you can cram in. It’s about choosing the right links that truly complement your content.
4. Choose Credible Sources
When you’re looking for sources to link to, aim high. Go for the big players in your industry – the ones with solid reputations and high authority. These could be well-known publications, respected industry blogs, or official organizational websites.
5. Make the Links Relevant
Context is king when it comes to linking. Each link should have a clear purpose and relate directly to what you’re talking about. If you’re writing about social media marketing, a link to a gardening website probably doesn’t make sense.
Don’t force links where they don’t belong. If you find yourself struggling to make a link fit, it’s probably not the right link for that piece of content.
6. Perform Regular Audits
Set aside time regularly to go through your links. Check if they’re still working – broken links are bad for user experience and SEO. Also, see if the content they’re linking to is still relevant and up to date.
7. Reach Out To Websites Directly
Don’t be shy about reaching out to other websites in your industry. Look for sites that complement your content and could benefit from linking to you.
When you reach out, focus on the value you can provide. Maybe you’ve got a great piece of content that their readers would find useful. Or perhaps you could offer to write a guest post for their blog.
Guidelines For Acquiring Quality External Links
Let’s talk about quality backlinks. They’re hard to get, but worth the effort. Let’s break down some effective external link-acquiring strategies.
1. Create Link-Worthy Content
This is the foundation of any solid link-building strategy. Quality content is like a magnet for links. Aim to create content that’s not just good but genuinely helpful and unique.
Comprehensive guides, original research, or in-depth analysis pieces tend to naturally attract links. Remember, if your content is valuable enough, people will want to share it.
2. Explore the Skyscraper Technique
This technique is all about taking great content and making it even better. Start by finding popular content in your niche that’s already attracting lots of links.
Then, create something even more valuable. Try adding more depth, updating outdated info, or improving the visuals.
After that, reach out to sites that are linked to the original piece and show them the improved version. It’s a win-win. They get to link to better content, and you get a quality backlink.
3. Guest Posting
Guest posting is still a powerful way to build quality links and expand your reach. Look for reputable sites in your industry that accept guest posts. The key is to pitch ideas that their audience will love, not just what you want to write about.
When done right, guest posting not only gets you a backlink but also puts you in front of a new audience. It’s a great way to build your authority in your field.
4. Share Your Expertise
Positioning yourself as an expert in your field can naturally attract links. Look for opportunities to share your knowledge. You can do it through interviews, expert roundups, or contributing quotes to articles.
When you’re recognized as an authority, people naturally want to link to your content. It’s also a great way to build your personal brand alongside your website’s authority.
For example, we have mentioned some of the big names in the SEO industry throughout this article. Matt Diggity, a well-known SEO expert shared valuable insights on silo structures.
We also referenced Kyle Roof’s simple yet effective silo technique which he demonstrated in an interview with Matt.
5. Be Patient And Persistent
Link building is a long-term game, not a quick fix. Keep refining your approach based on what works. Track your results and double down on successful tactics.
Avoid shortcuts or black hat techniques. They might work short-term but can tank your site long-term. Focus on creating genuine value and the links will follow.
Techniques For Effective External Link Outreach
External link outreach is a crucial part of any SEO strategy. It’s about connecting with other website owners and convincing them to link back to your site. When done right, it can significantly boost your site’s authority and visibility.
1. Personalize Your Approach
Generic, mass-produced emails won’t cut it. Take the time to research each site you’re reaching out to.
Mention something specific about their content or recent achievements. Show that you’ve done your homework and genuinely value their platform.
2. Offer Value, Not Just Requests
Don’t just ask for a link. Offer something valuable in return. This could be high-quality content, exclusive data, or even a mutually beneficial collaboration. Consider what the other site might need or want.
3. Follow Up Strategically
Don’t give up after one unanswered email. Follow up but do it smartly. Wait a reasonable amount of time (usually a week or two) before sending a polite reminder.
Keep your follow-up emails brief and to the point. Sometimes, people just need a gentle nudge to act on your initial request.
4. Leverage Social Media
Before sending an email, try to establish a connection on social media. Follow their accounts, engage with their content, and share their posts. This can warm up the relationship and make your outreach email feel less like a cold call.
5. Be Clear and Concise
Respect the recipient’s time by getting straight to the point. Clearly explain who you are, why you’re reaching out, and what you’re offering or requesting.
Use bullet points if necessary to make your email easily scannable. End with a clear call-to-action so the recipient knows exactly what you want them to do next.
Avoid These Common Errors With External Links
While external links can significantly boost your SEO and provide value to your readers, they can also be a source of trouble if not handled correctly. Make sure to avoid these common errors:
1. Linking to Low-Quality or Irrelevant Sites
Your external links reflect your site’s credibility. Linking to low-quality or irrelevant sites can harm your reputation and SEO efforts. Always vet the sites you’re linking to, ensuring they’re reputable and relevant to your content
2. Neglecting to Use NoFollow Tags When Necessary
Not all links should pass link equity. Use NoFollow tags for affiliate links, user-generated content, or when linking to sites you don’t fully trust. This helps maintain a natural link profile and complies with search engine guidelines.
3. Ignoring Broken External Links
Regularly audit your external links. Remove or replace any that are no longer working. Consider using automated tools to check for broken links periodically.
4. Overusing Exact Match Anchor Text
While descriptive anchor text is important, using too many exact match keywords can look unnatural and may trigger spam filters. Mix up your anchor text with branded terms, partial matches, and natural language variations.
5. Not Opening External Links in New Tabs
When users click an external link that opens in the same tab, you risk losing them from your site. Set external links to open in new tabs to keep your site open in the background.
Avoid These Common Errors With Internal Links
Even with internal links, you need to be careful. We have already covered the benefits of doing proper internal links, but there are several common mistakes that can undermine these benefits. Let’s explore 8 errors to avoid when implementing internal links:
1. Overusing Internal Links
Too many can overwhelm readers and dilute the value of each link. Aim for balance. Include enough links to guide users and search engines, but not so many that your content becomes cluttered.
2. Using Generic Anchor Text
Avoid vague anchor text like “click here” or “read more”. Instead, use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text that gives users and search engines a clear idea of what the linked page is about.
3. Neglecting Inner Pages
Don’t just link to your homepage and main category pages. Include links to inner, more specific pages within your site. This helps distribute link juice throughout your site.
But let’s be real. Managing all these internal links can be a headache. That’s where LinkBoss comes in handy. Want to give your inner pages the attention they deserve?
LinkBoss can help you find and create relevant internal links automatically. Sign up today and say goodbye to all those orphan posts
4. Ignoring Relevance
Internal links should always be contextually relevant. Don’t force links where they don’t naturally fit. Each link should make sense within the content it’s placed in and provide additional value to the reader interested in that topic.
5. Failing to Update Internal Links
As your site grows and changes, some pages may be removed, or URLs altered. Regularly audit your internal links to ensure they’re not leading to dead ends or outdated content.
6. Overlooking Opportunities in Old Content
Don’t forget about your older content. Periodically review and update older posts or pages with links to newer, relevant content. This keeps your older content fresh and helps distribute link equity to your newer pages.
7. Using NoFollow on Internal Links
Unlike with some external links, there’s generally no need to use NoFollow attributes on internal links. Doing so prevents the flow of link equity within your own site.
8. Neglecting a Clear Hierarchy
Your internal linking structure should reflect a clear hierarchy of information on your site. Make sure your most important pages receive more internal links.
What Is A Balanced Linking Strategy: Why It’s Important
A balanced linking strategy is crucial for effective website navigation and SEO performance. Ever wondered why some websites feel like a maze while others are a breeze to navigate?
It’s all about the linking strategy. Let’s break down what a balanced approach looks like and why it matters. A balanced linking strategy involves:
- Appropriate use of internal links
- Strategic placement of external links
- Optimizing for user experience and SEO
So, why is it important? See the reasons below:
Enhanced User Engagement
A well-structured linking strategy keeps visitors on your site longer. It guides them through relevant content, improving overall engagement.
Improved SEO Performance
Search engines use links to understand your site structure. A balanced approach helps them crawl and index your content more effectively.
Increased Credibility
Linking to reputable external sources can boost your site’s authority. It demonstrates your connection to valuable industry resources.
Better User Navigation
Clear internal linking helps users find information easily. It creates a logical path through your content, enhancing user experience.
Implementing a Balanced Linking Strategy
Prioritize internal links to keep users on your site. Use descriptive, relevant anchor text. Focus on quality over quantity in link placement. Place external links thoughtfully. Also, consider a dedicated section for external resources.
The Wikipedia Model
Wikipedia’s approach to linking is worth noting:
- Content links are primarily internal
- External links are grouped in a separate section
This method provides clarity and maintains user focus.
Internal vs External: Finding the Right Balance
Internal links form the core of your linking strategy. They guide users through your site and distribute page authority. External links should be used judiciously to support your content and build credibility.
And that wraps up our article on internal vs external links. So, which is more important? The answer would be both. However, for most sites, internal links should be the primary focus.
That being said, the key is finding the right balance between internal and external linking. However, managing this balance effectively can be time-consuming and complex.
That’s where LinkBoss comes in handy. This AI-powered tool analyzes your content and suggests relevant internal links. You can implement complex silos in a couple of minutes.
Want to optimize your internal linking without manual effort? Consider giving LinkBoss a try. Sign up now for a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Where Should Internal Links Be Placed On A Website?
Internal links should be placed strategically throughout your content. Include them in navigation menus, body text, and footers. The key is to add links where they provide value and improve user navigation.
2. What’s The Difference Between Inbound And Outbound Links?
Inbound links come from external websites to your site. Outbound links go from your site to external websites.
3. How Do I Find External Links To My Website?
Use tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO tools like Ahrefs and Semrush. These tools can provide reports on websites linking to yours.
4. When To Use An External Link?
Use external links to cite sources or provide additional information. Link to reputable websites that offer value to your readers. Consider opening external links in new tabs to keep users on your site.
5. How Many Internal Links Are Too Many?
There’s no strict rule but avoid overwhelming your content with links. Focus on quality over quantity. Each link should serve a purpose. If links start to disrupt readability, you may need to reduce them.